|
Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins control vacuole trafficking and developmental programs through the regulation of lipid metabolism
Saturday, 2015/01/10 | 08:34:40
|
|
Ruixi Li, Ruobai Sun, Glenn R. Hicks, and Natasha V. Raikhel1 Department of Botany and Plant Sciences, Center for Plant Cell Biology, Institute for Integrative Genome Biology, University of California, Riverside, CA 92521 SignificanceAuxin is an important phytohormone that regulates almost all aspects of plant growth and development. Ribosome proteins serve as translational regulators of auxin response. This work highlights the significance of lipid metabolism in the downstream of ribosome protein function to link auxin-regulated developmental patterning with endomembrane trafficking. Our work sheds light on a novel link between auxin signaling, ribosome function, and lipid metabolism. AbstractThe vacuole is the most prominent compartment in plant cells and is important for ion and protein storage. In our effort to search for key regulators in the plant vacuole sorting pathway, ribosomal large subunit 4 (rpl4d) was identified as a translational mutant defective in both vacuole trafficking and normal development. Polysome profiling of the rpl4d mutant showed reduction in polysome-bound mRNA compared with wild-type, but no significant change in the general mRNA distribution pattern. Ribsomal profiling data indicated that genes in the lipid metabolism pathways were translationally down-regulated in the rpl4d mutant. Live imaging studies by Nile red staining suggested that both polar and nonpolar lipid accumulation was reduced in meristem tissues of rpl4d mutants. Pharmacological evidence showed that sterol and sphingolipid biosynthetic inhibitors can phenocopy the defects of the rpl4d mutant, including an altered vacuole trafficking pattern. Genetic evidence from lipid biosynthetic mutants indicates that alteration in the metabolism of either sterol or sphingolipid biosynthesis resulted in vacuole trafficking defects, similar to the rpl4d mutant. Tissue-specific complementation with key enzymes from lipid biosynthesis pathways can partially rescue both vacuole trafficking and auxin-related developmental defects in the rpl4d mutant. These results indicate that lipid metabolism modulates auxin-mediated tissue differentiation and endomembrane trafficking pathways downstream of ribosomal protein function.
See: http://www.pnas.org/content/112/1/E89.abstract.html?etoc PNAS January 6, 2015; vol.112, no.1: E89–E98
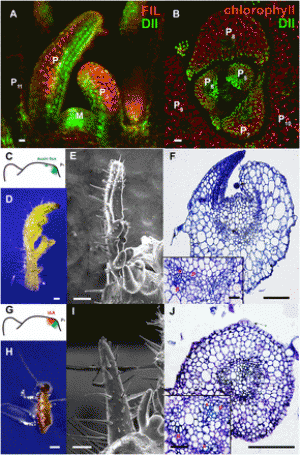
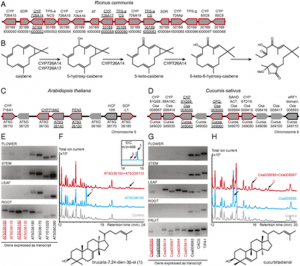
Fig. 1. Lipid metabolism genes were translational down-regulated in rpl4d mutants. (A) Images of hypocotyl cells from RFP:CTPP lines in the background of Col or rpl4d mutant. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (B) A254 absorption profiles of total polysomes from 7-d-old seedlings of Col and rpl4d mutants. Larger fraction numbers correspond to higher sucrose concentrations. Red frame indicates sucrose gradient corresponding to polysome bound mRNA. (C) Metabolism catalogs of pathways according to GO classification. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
.gif)