|
Genetic Architecture of Domestication-Related Traits in Maize.
Wednesday, 2016/07/20 | 08:09:41
|
|
Xue S, Bradbury P, Casstevens T, Holland JB. Genetics. 2016 Jul 13. pii: genetics.116.191106. [Epub ahead of print] AbstractStrong directional selection occurred during the domestication of maize from its wild ancestor teosinte, reducing its genetic diversity, particularly at genes controlling domestication-related traits. Nevertheless, variability for some domestication-related traits is maintained in maize. The genetic basis of this could be sequence variation at the same key genes controlling maize-teosinte differentiation (due to lack of fixation or arising as new mutations after domestication), distinct loci with large effects, or polygenic background variation. Previous studies permit annotation of maize genome regions associated with the major differences between maize and teosinte or that exhibit population genetic signals of selection during either domestication or post-domestication improvement. Genome-wide association studies and genetic variance partitioning analyses were performed in two diverse maize inbred line panels to compare the phenotypic effects and variances of sequence polymorphisms in regions involved in domestication and improvement to the rest of the genome. Additive polygenic models explained most of the genotypic variation for domestication-related traits; no large effect loci were detected for any trait. Most trait variance was associated with background genomic regions lacking previous evidence for involvement in domestication. Improvement sweep regions were associated with more trait variation than expected based on the proportion of the genome they represent. Selection during domestication eliminated large effect genetic variants that would revert maize toward a teosinte type. Small effect polygenic variants (enriched in the improvement sweep regions of the genome) are responsible for most of the standing variation for domestication-related traits in maize.
See: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27412713
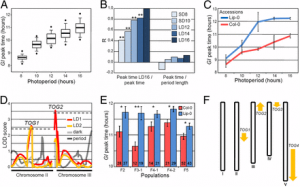
Figure 6: Best linear unbiased estimates (BLUEs) for cob length of NAM lines. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(40).png)