|
Major genes determining yield-related traits in wheat and barley
Friday, 2017/06/16 | 07:56:57
|
|
Anna Nadolska-Orczyk, Izabela K. Rajchel, Wacław Orczyk, Sebastian Gasparis Theoretical and Applied Genetics; June 2017, Volume 130, Issue 6, pp 1081–1098 AbstractKey messageCurrent development of advanced biotechnology tools allows us to characterize the role of key genes in plant productivity. The implementation of this knowledge in breeding strategies might accelerate the progress in obtaining high-yielding cultivars. AbstractThe achievements of the Green Revolution were based on a specific plant ideotype, determined by a single gene involved in gibberellin signaling or metabolism. Compared with the 1950s, an enormous increase in our knowledge about the biological basis of plant productivity has opened new avenues for novel breeding strategies. The large and complex genomes of diploid barley and hexaploid wheat represent a great challenge, but they also offer a large reservoir of genes that can be targeted for breeding. We summarize examples of productivity-related genes/mutants in wheat and barley, identified or characterized by means of modern biology. The genes are classified functionally into several groups, including the following: (1) transcription factors, regulating spike development, which mainly affect grain number; (2) genes involved in metabolism or signaling of growth regulators—cytokinins, gibberellins, and brassinosteroids—which control plant architecture and in consequence stem hardiness and grain yield; (3) genes determining cell division and proliferation mainly impacting grain size; (4) floral regulators influencing inflorescence architecture and in consequence seed number; and (5) genes involved in carbohydrate metabolism having an impact on plant architecture and grain yield. The implementation of selected genes in breeding programs is discussed, considering specific genotypes, agronomic and climate conditions, and taking into account that many of the genes are members of multigene families.
See: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00122-017-2880-x
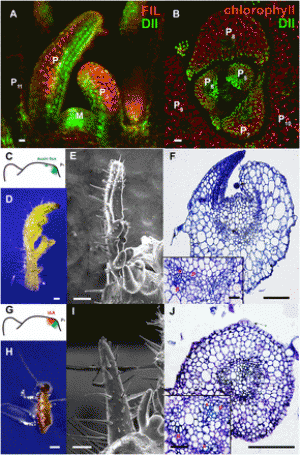
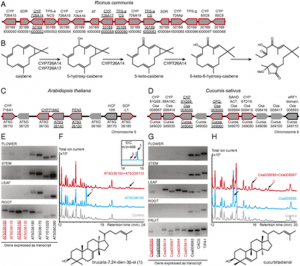
Fig. 1 Major genes determining plant architecture in barley (left) and wheat (right). Vertical arrows indicate down or up enzyme regulation/gene expression; horizontal arrows indicate direction of gene co-regulation; bold main/key allele; ellipsis multiple alleles |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(42).png)