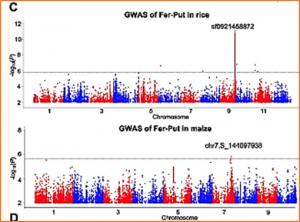
Plants orchestrate drought responses at metabolic level but the genetic basis remains elusive in rice. In this study, 233 drought-responsive metabolites (DRMs) were quantified in a large rice population comprised of 510 diverse accessions at the reproductive stage. Large metabolic variations in drought responses were detected, and little correlation of metabolic levels between drought and normal conditions were observed. Interestingly, most of these DRMs could predict drought resistance in high accuracy.
Salt stress is the second most devastating abiotic stress after drought and limits rice production globally. Genetic enhancement of salinity tolerance is a promising and cost-effective approach to achieve yield gains in salt-affected areas. Breeding for salinity tolerance is challenging because of the genetic complexity of the response of rice plants to salt stress, as it is governed by minor genes with low heritability and high G × E interactions.
The development of future food is an inevitable task for sustainable humanity. Unfortunately, the future food candidates reported so far have practical limitations in terms of commercialization, such as nutritional imbalance, unfamiliar taste, and poor formability. Accordingly, this study proposes to develop a new food ingredient in which rice grains, nanocoating, and animal cells are integrated.
The brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), a rice-specific pest, has risen to the top of the list of significant pathogens and insects in recent years. Host plant-mediated resistance is an efficient strategy for BPH control. Nonetheless, BPH resistance in rice cultivars has succumbed to the emergence of distinct virulent BPH populations. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a pivotal role in regulating plant-environment interactions;
Powdery mildew is one of the most severe fungal diseases reducing yield and quality of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.) and other cucurbit crops. Genes responsible for powdery mildew resistance in watermelon are highly valuable. In this study, we first identified the QTL pm-lox for powdery mildew resistance in watermelon, located within a 0.93 Mb interval of chromosome 2, via XP-GWAS method using two F2 populations.
The full-length CDS of GhRCAβ2 was 1317 bp, and it encoded a protein with a chloroplast transit peptide. The GhRCAβ2 had two conserved ATP-binding domains, and did not have the C-terminal extension (CTE) domain that was unique to the RCA α-isoform in plants. Evolutionarily, GhRCAβ2 was clustered in Group A, and had a close evolutionary relationship with the soybean RCA.
The amount of free asparagine in grain of a wheat genotype determines its potential to form harmful acrylamide in derivative food products. Here, we explored the variation in the free asparagine, aspartate, glutamine and glutamate contents of 485 accessions reflecting wheat worldwide diversity to define the genetic architecture governing the accumulation of these amino acids in grain.
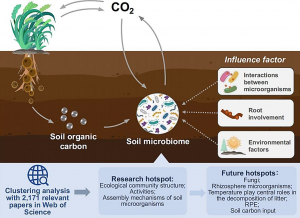
Soil microorganisms, by actively participating in the decomposition and transformation of organic matter through diverse metabolic pathways, play a pivotal role in carbon cycling within soil systems and contribute to the stabilization of organic carbon, thereby influencing soil carbon storage and turnover. Investigating the processes, mechanisms, and driving factors of soil microbial carbon cycling is crucial for understanding the functionality of terrestrial carbon sinks and effectively addressing climate change. This review comprehensively discusses the role of soil microorganisms in soil carbon cycling from three perspectives: metabolic pathways, microbial communities, and environmental influences.
Chilling tolerance in crops can increase resilience through longer growing seasons, drought escape, and nitrogen use efficiency. In sorghum (Sorghum bicolor [L.] Moench), breeding for chilling tolerance has been stymied by coinheritance of the largest-effect chilling tolerance locus, qSbCT04.62, with the major gene underlying undesirable grain proanthocyanidins, WD40 transcriptional regulator Tannin1. To test if this coinheritance is due to antagonistic pleiotropy of Tannin1, we developed and studied near-isogenic lines (NILs) carrying chilling tolerant haplotypes at qCT04.62.
Aphanomyces root rot, caused by Aphanomyces euteiches, is the most important disease of pea (Pisum sativum L.) worldwide. The development of pea-resistant varieties is a major challenge to control the disease. Previous linkage studies identified seven main resistance quantitative trait loci (QTL), including the QTL Ae-Ps4.5 associated with partial resistance in US nurseries infested by the pea pathotype III of A. euteiches. This study aimed to confirm the major effect of Ae-Ps4.5 on A. euteiches pathotype III, refine its interval, and identify candidate genes underlying the QTL.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :