The endophytic microbiome plays an important role in plant health and pathogenesis. However, little is known about its relationship with bacterial blight (BB) of rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). The current study compared the community compositional structure of the endophytic microbiota in healthy and BB symptomatic leaves of rice through a metabarcoding approach, which revealed BB induced a decrease in the alpha-diversity of the fungal communities and an increase in the bacterial communities.
In this study, we report the functional characterization of VvNPF6.5, a member of nitrate transporter 1/peptide transporter family (NRT1/PTR/NPF) in Vitis vinifera. Subcellular localization in Arabidopsis protoplasts indicated that VvNPF6.5 is plasma membrane localized. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis indicated that VvNPF6.5 is expressed predominantly in roots and stems and its expression is rapidly induced by nitrate.
Determinate and indeterminate growth habits of cucumber can affect plant architecture and crop yield. The TERMINAL FLOWER 1 (TFL1) controls determinate/indeterminate growth in Arabidopsis. In this study, a novel mutation in cucumber TFL1 homolog (CsCEN) has shown to regulate determinate growth and product of terminal flowers in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), which is similar to the function of CsTFL1 as previously reported.
Banana is an important fruit and food crop, but is threatened by Fusarium wilt, one of the most devastating soil-borne fungal diseases. Only host resistance facilitates banana cultivation in infested soils around the world, but the genetic basis of Fusarium wilt of banana (FWB) is unknown. We selfed a heterozygous wild banana accession Musa acuminata ssp. malaccensis (Mam, AA, 2n = 22) to generate a mapping population and to investigate the inheritance of resistance to Race 1 and tropical race 4 (TR4) that cause FWB
Quantitative disease resistance (QDR) toward Phytophthora sojae in soybean is a complex trait controlled by many small-effect loci throughout the genome. Along with the technical and rate-limiting challenges of phenotyping resistance to a root pathogen, the trait complexity can limit breeding efficiency. However, the application of genomic prediction to traits with complex genetic architecture, such as QDR toward P. sojae, is likely to improve breeding efficiency.
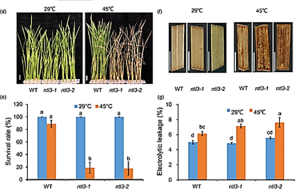
Heat stress induces misfolded protein accumulation in endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which initiates the unfolded protein response (UPR) in plants. Previous work has demonstrated the important role of a rice ER membrane-associated transcription factor OsbZIP74 (also known as OsbZIP50) in UPR. However, how OsbZIP74 and other membrane-associated transcription factors are involved in heat stress tolerance in rice is not reported.
The autopolyploid nature of potato and sweetpotato ensures a wide range of meiotic configurations and linkage phases leading to complex gene-action and pose problems in genotype data quality and genomic selection analyses. We used a 315-progeny biparental F1 population of hexaploid sweetpotato and a diversity panel of 380 tetraploid potato, genotyped using different platforms to answer the following questions: (i) do polyploid crop breeders need to invest more for additional sequencing depth? (ii) how many markers are required to make selection decisions? (iii) does considering non-additive genetic effects improve predictive ability (PA)? (iv) does considering dosage or quantitative trait loci (QTL) offer significant improvement to PA?
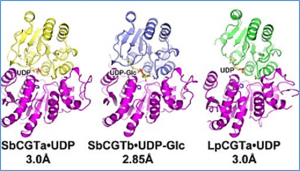
Schaftoside and isoschaftoside are bioactive natural products widely distributed in higher plants including cereal crops and medicinal herbs. Their biosynthesis may be related with plant defense. However, little is known on the glycosylation biosynthetic pathway of these flavonoid di-C-glycosides with different sugar residues. Herein, we report that the biosynthesis of (iso)schaftosides is sequentially catalyzed by two C-glycosyltransferases (CGTs), i.e., CGTa for C-glucosylation of the 2-hydroxyflavanone aglycone and CGTb for C-arabinosylation of the mono-C-glucoside.
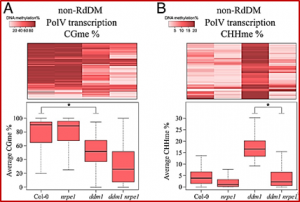
Eukaryotic genomes are pervasively transcribed, yet most transcribed sequences lack conservation or known biological functions. In Arabidopsis thaliana, RNA polymerase V (Pol V) produces noncoding transcripts, which base pair with small interfering RNA (siRNA) and allow specific establishment of RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) on transposable elements. Here, we show that Pol V transcribes much more broadly than previously expected,
Peanut is widely grown and provides protein and edible oil for millions of people. Peanut growth and productivity are frequently negatively affected by abiotic and biotic environmental factors. However, the research on improving peanut germplasm resources by genetic transformation is very limited. Here, the novel R2R3-MYB repressor GmMYB3a was introduced into peanut plants by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation for the first time for thorough evaluation of the function of GmMYB3a in drought stress plant responses. We generated GmMYB3a-transgenic peanut plants.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :