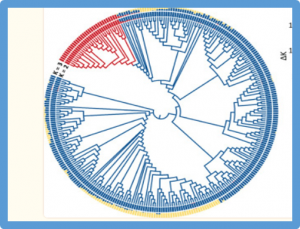
Barley yellow dwarf (BYD) is one of the economically most important virus diseases of cereals worldwide, causing yield losses up to 80%. The means to control BYD are limited, and the use of genetically resistant cultivars is the most economical and environmentally friendly approach. The objectives of this study were i) to identify the causative gene for BYD virus (BYDV)-PAV resistance in maize, ii) to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms and/or structural variations in the gene sequences,
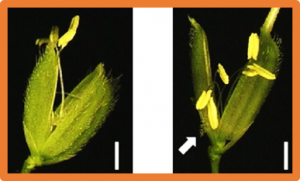
The concave shape of the fruit tip in pepper plants is highly susceptible to drought and low temperature stresses, resulting in the appearance of a pointed tip fruit, which affects its commercial value. However, few studies on the process of fruit tip development and regulatory genes in pepper have been reported. Herein, the developmental process of the ovary before anthesis, especially changes in the shape of the ovary tip, was studied in detail.
Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae biovar 3 (Psa3) causes a devastating canker disease in yellow-fleshed kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis). The effector HopZ5, which is present in all isolates of Psa3 causing global outbreaks of pandemic kiwifruit canker disease, triggers immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana and is not recognised in susceptible A. chinensis cultivars. In a search for N. benthamiana nonhost resistance genes against HopZ5
Rice blast is a destructive fungal disease affecting rice plants at various growth stages, significantly threatening global yield stability. Development of resistant rice cultivars stands as a practical means of disease control. Generally, association mapping with a diversity panel powerfully identifies new alleles controlling trait of interest. On the other hand, utilization of a breeding panel has its advantage that can be directly applied in a breeding program. In this study, we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) for blast resistance using 296 commercial rice cultivars with low population structure but large phenotypic diversity.
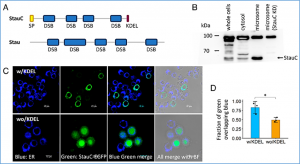
RNA interference (RNAi) is more efficient in coleopteran insects than other insects. StaufenC (StauC), a coleopteran-specific double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding protein, is required for efficient RNAi in coleopterans. We investigated the function of StauC in the intracellular transport of dsRNA into the cytosol, where dsRNA is digested by Dicer enzymes and recruited by Argonauts to RNA-induced silencing complexes. Confocal microscopy and cellular organelle fractionation studies have shown that dsRNA is trafficked through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in coleopteran Colorado potato beetle (CPB) cells.
Examining the connection between P and starch-related signals can help elucidate the balance between nutrients and yield. This study utilized 307 diverse maize inbred lines to conduct multi-year and multi-plot trials, aiming to explore the relationship among P content, starch content, and 100-kernel weight (HKW) of mature grains. A significant negative correlation was found between P content and both starch content and HKW, while starch content showed a positive correlation with HKW.
Sugarcane, the world's most harvested crop by tonnage, has shaped global history, trade and geopolitics, and is currently responsible for 80% of sugar production worldwide1. While traditional sugarcane breeding methods have effectively generated cultivars adapted to new environments and pathogens, sugar yield improvements have recently plateaued2.
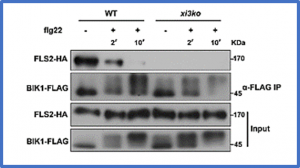
Plants rely on immune receptor complexes at the cell surface to perceive microbial molecules and transduce these signals into the cell to regulate immunity. Various immune receptors and associated proteins are often dynamically distributed in specific nanodomains on the plasma membrane (PM). However, the exact molecular mechanism and functional relevance of this nanodomain targeting in plant immunity regulation remain largely unknown.
Temperate Geng/Japonica (GJ) rice yields have improved significantly, bolstering global food security. However, GJ rice breeding faces challenges, including enhancing grain quality, ensuring stable yields at warmer temperatures, and utilizing alkaline land. In this study, we employed CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology to knock out the GS3 locus in seven elite GJ varieties with superior yield performance.
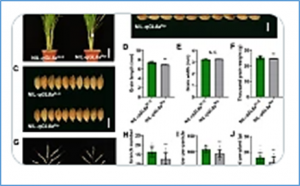
Grain size is a crucial agronomic trait that determines grain weight and final yield. Although several genes have been reported to regulate grain size in rice (Oryza sativa), the function of Wall-Associated Kinase family genes affecting grain size is still largely unknown. In this study, we identified GRAIN WEIGHT AND NUMBER 1 (GWN1) using map-based cloning. GWN1 encodes the OsWAK74 protein kinase, which is conserved in plants.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :