Seed vigor is an important trait in crop breeding; however, the underlying molecular regulatory mechanisms governing this trait in rapeseed remain largely unknown. In the present study, vigor-related traits were analyzed in seeds from a doubled haploid (DH) rapeseed (Brassica napus) population grown in 2 different environments using seeds stored for 7, 5, and 3 years under natural storage conditions.
Abiotic stresses limit the quantity and quality of rice grain production, which is considered a strategic crop in many countries. In this study, a meta-analysis of different microarray data at seedling stage was performed to investigate the effects of multiple abiotic stresses (drought, salinity, cold situation, high temperature, alkali condition, iron, aluminum, and heavy metal toxicity, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium deficiency) on rice. Comparative analysis between multiple abiotic stress groups and their control groups indicated 561 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), among which 422 and 139 genes were up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively.
Strigolactones (SLs) are a new class of plant hormones that play a significant role in regulating various aspects of plant growth promotion, stress tolerance and influence the rhizospheric microbiome. GR24 is a synthetic SL analog used in scientific research to understand the effects of SL on plants and to act as a plant growth promoter. This study aimed to conduct hormonal seed priming at different concentrations of GR24 (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 5.0 and 10.0 µM with and without arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation in selected aerobic rice varieties (CR Dhan 201, CR Dhan 204, CR Dhan 205, and CR Dhan 207),
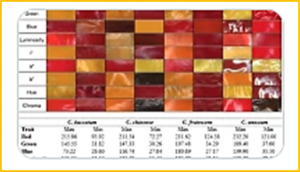
Peppers (Capsicum spp.) rank among the most widely consumed spices globally. Fruit color, serving as a determinant for use in food colorants and cosmeceuticals and an indicator of nutritional contents, significantly influences market quality and price. Cultivated Capsicum species display extensive phenotypic diversity, especially in fruit coloration.
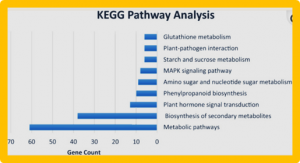
Improving the quality of the appearance of rice is critical to meet market acceptance. Mining putative quality-related genes has been geared towards the development of effective breeding approaches for rice. In the present study, two SL-GWAS (CMLM and MLM) and three ML-GWAS (FASTmrEMMA, mrMLM, and FASTmrMLM) genome-wide association studies were conducted in a subset of 3K-RGP consisting of 198 rice accessions with 553,831 SNP markers
This study aimed to investigate the effects of different proportions of dietary fermented sweet potato residue (FSPR) supplementation as a substitute for corn on the nutrient digestibility, meat quality, and intestinal microbes of yellow-feathered broilers. Experiment 1 (force-feeding) evaluated the nutrient composition and digestibility of mixtures with different proportions of sweet potato residue (70%, 80%, 90%, and 100%) before and after fermentation.
Haplotype-resolved genome assemblies were produced for Chasselas and Ugni Blanc, two heterozygous Vitis vinifera cultivars by combining high-fidelity long-read sequencing and high‐throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C). The telomere-to-telomere full coverage of the chromosomes allowed us to assemble separately the two haplo-genomes of both cultivars and revealed structural variations between the two haplotypes of a given cultivar.
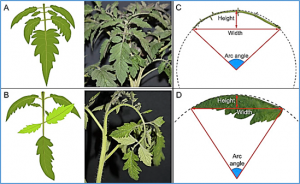
Leaf angle is a crucial trait in plant architecture that plays an important role in achieving optimal plant structure. However, there are limited reports on gene localization, cloning, and the function of plant architecture in horticultural crops, particularly regarding leaf angle. In this study, we selected ‘Z3’ with erect leaves and ‘Heinz1706’ with horizontal leaves as the phenotype and cytological observation.
Pectin is a structural polysaccharide and a major component of plant cell walls. Pectate lyases are a class of enzymes that degrade demethylated pectin by cleaving the α-1,4-glycosidic bond, and they play an important role in plant growth and development. Currently, little is known about the PL gene family members and their involvement in salt stress in potato. In this study, we utilized bioinformatics to identify members of the potato pectate lyase gene family and analyzed their gene and amino acid sequence characteristics.
Structural variants (SVs) have been reported to impose major effects on agronomic traits, representing a significant contributor to crop domestication. However, the landscape of SVs between wild and cultivated melons is elusive and how SVs have contributed to melon domestication remains largely unexplored. Here, we report a 379-Mb chromosome-scale genome of a wild progenitor melon accession “P84”, with a contig N50 of 14.9 Mb


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :