Identification and functional marker development of SbPLSH1 conferring purple leaf sheath in sorghum
The purple leaf sheath of sorghum, a trait mostly related to anthocyanin deposition, is a visually distinguishable morphological marker widely used to evaluate the purity of crop hybrids. We aimed to dissect the genetic mechanism for leaf sheath color to mine the genes regulating this trait. In this study, two F2 populations were constructed by crossing a purple leaf sheath inbred line (Gaoliangzhe) with two green leaf sheath inbred lines (BTx623 and Silimei).
Reproductive phasiRNAs (phased, small interfering RNAs) are broadly present in angiosperms and play crucial roles in sustaining male fertility. While the premeiotic 21-nt (nucleotides) phasiRNAs and meiotic 24-nt phasiRNA pathways have been extensively studied in maize (Zea mays) and rice (Oryza sativa), a third putative category of reproductive phasiRNAs–named premeiotic 24-nt phasiRNAs–have recently been reported in barley (Hordeum vulgare) and wheat (Triticum aestivum).
A technique for chromosomal insertion of large DNA segments is much needed in plant breeding and synthetic biology to facilitate the introduction of desired agronomic traits and signaling and metabolic pathways. Here we describe PrimeRoot, a genome editing approach to generate targeted precise large DNA insertions in plants. Third-generation PrimeRoot editors employ optimized prime editing guide RNA designs, an enhanced plant prime editor and superior recombinases to enable precise large DNA insertions of up to 11.1 kilobases into plant genomes.
Decreased production of crops due to climate change has been predicted scientifically. While climate-resilient crops are necessary to ensure food security and support sustainable agriculture, predicting crop growth under future global warming is challenging. Therefore, we aimed to assess the impact of realistic global warming conditions on rice cultivation. We developed a crop evaluation platform, the agro-environment (AE) emulator, which generates diverse environments by implementing the complexity of natural environmental fluctuations in customized, fully artificial lighting growth chambers.
Cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis) is a distinctive vegetable that supplies a nutrient-rich edible inflorescence meristem for the human diet. However, the genomic bases of its selective breeding have not been studied extensively. Herein, we present a high-quality reference genome assembly C-8 (V2) and a comprehensive genomic variation map consisting of 971 diverse accessions of cauliflower and its relatives.
The potato cyst nematodes (PCN) Globodera pallida and Globodera rostochiensis are economically important potato pests in almost all regions where potato is grown. One important management strategy involves deployment through introgression breeding into modern cultivars of new sources of naturally occurring resistance from wild potato species. We describe a new source of resistance to G. pallida from wild potato germplasm.
In commercial maize breeding, doubled haploid (DH) technology is arguably the most efficient resource for rapidly developing novel, completely homozygous lines. However, the DH strategy, using in vivo haploid induction, currently requires the use of mutagenic agents which can be not only hazardous, but laborious. This study focuses on an alternative approach to develop DH lines—spontaneous haploid genome duplication (SHGD) via naturally restored haploid male fertility (HMF)
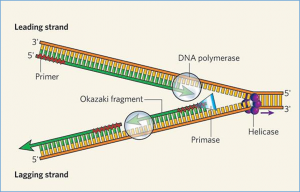
Chromatin replication is intricately intertwined with the recycling of parental histones to the newly duplicated DNA strands for faithful genetic and epigenetic inheritance. The transfer of parental histones occurs through two distinct pathways: leading strand deposition, mediated by the DNA polymerase ε subunits Dpb3/Dpb4, and lagging strand deposition, facilitated by the MCM helicase subunit Mcm2.
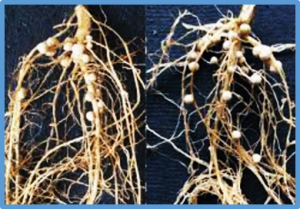
Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legume nodules requires substantial energy investment from host plants, and soybean (Glycine max (L.) supernodulation mutants show stunting and yield penalties due to overconsumption of carbon sources. We obtained soybean mutants differing in their nodulation ability, among which rhizobially induced cle1a/2a (ric1a/2a) has a moderate increase in nodule number, balanced carbon allocation, and enhanced carbon and nitrogen acquisition
Seed germination represents a multifaceted biological process influenced by various intrinsic and extrinsic factors. In the present study, our investigation unveiled the regulatory role of OsSCYL2, a gene identified as a facilitator of seed germination in rice. Notably, the germination kinetics of OsSCYL2-overexpressing seeds surpassed those of their wild-type counterparts, indicating the potency of OsSCYL2 in enhancing this developmental process. Moreover, qRT-PCR results showed that OsSCYL2 was consistently expressed throughout the germination process in rice.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :