White bulb colors in onion (Allium cepa L.) are determined by either the C or I loci. The causal gene for the C locus was previously isolated, but the gene responsible for the I locus has not been identified yet. To identify candidate genes for the I locus, an approximately 7-Mb genomic DNA region harboring the I locus was obtained from onion and bunching onion (A. fistulosum) whole genome sequences using two tightly linked molecular markers
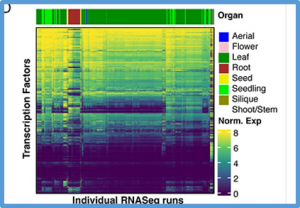
Organ-specific gene expression datasets that include hundreds to thousands of experiments allow the reconstruction of organ-level gene regulatory networks (GRNs). However, creating such datasets is greatly hampered by the requirements of extensive and tedious manual curation. Here, we trained a supervised classification model that can accurately classify the organ-of-origin for a plant transcriptome.
Sustainable farming on ever-shrinking agricultural land and declining water resources for the growing human population is one of the greatest environmental and food security challenges of the 21st century. Conventional, age-old organic farming practices alone, and foods based on costly cellular agriculture, do not have the potential to be upscaled to meet the food supply challenges for feeding large populations.
The B-box (BBX) gene family includes zinc finger protein transcription factors that regulate a multitude of physiological and developmental processes in plants. While BBX gene families have been previously determined in various plants, the members and roles of peanut BBXs are largely unknown. In this research, on the basis of the genome-wide identification of BBXs in three peanut species (Arachis hypogaea, A. duranensis, and A. ipaensis), we investigated the expression profile of the BBXs in various tissues and in response to salt and drought stresses and selected AhBBX6 for functional characterization.
Peanut is an important cash crop used in oil, food and feed in our country. The rapid development of sequencing technology has promoted the research on the related aspects of peanut genetic breeding. This paper reviews the research progress of peanut origin and evolution, genetic breeding, molecular markers and their applications, genomics, QTL mapping and genome selection techniques. The main problems of molecular genetic breeding in peanut research worldwide include: the narrow genetic resources of cultivated species, unstable genetic transformation and unclear molecular mechanism of important agronomic traits.
Trichomes, which are differentiated from epidermal cells, are special accessory structures that cover the above-ground organs of plants and possibly contribute to biotic and abiotic stress resistance. Here, a bulked segregant analysis (BSA) of an F2 population with significant variations in trichome length was undertaken. A 1.84-Mb candidate region on chromosome 10 was associated with trichome length. Resequencing and fine-mapping analyses indicated that a 12-kb structural variation in the promoter of Cla97C10G203450 (ClLOG) led to a significant expression difference in this gene in watermelon lines with different trichome lengths.
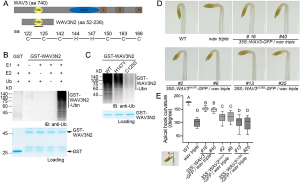
Auxin regulates plant growth and development through downstream signaling pathways, including the best-known SCFTIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA-ARF pathway and several other less characterized “noncanonical” pathways. Recently, one SCFTIR1/AFB-independent noncanonical pathway, mediated by Transmembrane Kinase 1 (TMK1), was discovered through the analyses of its functions in Arabidopsis apical hook development.
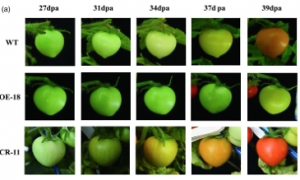
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) stands as one of the most valuable vegetable crops globally, and fruit firmness significantly impacts storage and transportation. To identify genes governing tomato firmness, we scrutinized the firmness of 266 accessions from core collections. Our study pinpointed an ethylene receptor gene, SlEIN4, located on chromosome 4 through a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of fruit firmness in the 266 tomato core accessions. A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (A → G) of SlEIN4 distinguished lower (AA) and higher (GG) fruit firmness genotypes.
The single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus Broad bean wilt virus 2 (BBWV2) causes substantial damage to pepper (Capsicum annuum) cultivation. Here, we describe mapping the BBWV2 resistance locus bwvr using a F7:8 recombinant inbred line (RIL) population constructed by crossing the BBWV2-resistant pepper accession ‘SNU-C’ with the susceptible pepper accession ‘ECW30R.’ All F1 plants infected with the BBWV2 strain PAP1 were susceptible to the virus, and the RIL population showed a 1:1 ratio of resistance to susceptibility, indicating that this trait is controlled by a single recessive gene.
Photosynthesis is one of the main factors determining crop yield. A better understanding of the genetic architecture for photosynthesis is of great significance for soybean yield improvement. Our previous studies identified 5,410,112 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from the resequencing data of 219 natural soybean accessions. Here, we identified 634,106 insertions and deletions (InDels) from these 219 accessions and used these InDel variations to perform principal component and linkage disequilibrium analysis of this population.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :