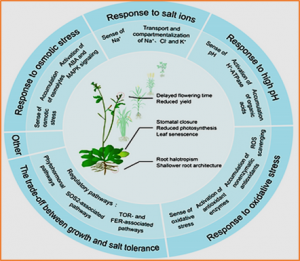
Excess soil salinity affects large regions of land and is a major hindrance to crop production worldwide. Therefore, understanding the molecular mechanisms of plant salt tolerance has scientific importance and practical significance. In recent decades, studies have characterized hundreds of genes associated with plant responses to salt stress in different plant species. These studies have substantially advanced our molecular and genetic understanding of salt tolerance in plants and have introduced an era of molecular design breeding of salt-tolerant crops.
Colorless silk is a key characteristic contributing to the visual quality of fresh corn intended for market distribution. Nonetheless, the identification of Mendelian trait loci and associated genes that control silk color has been scarce. In this study, a F2 population arising from the hybridization of the single-segment substitution line qSRC3MT1 with red silk, carrying an introgressed allele from teosinte (Zea mays ssp. mexicana),
Potatoes produce two major steroidal glycoalkoids α-solanine and α-chaconine that comprise about 95% of all the glycoalkaloids in the potatoes. Under the stressful conditions production of glycoalkaloids get amplified that can lead to toxic symptoms in humans, particularly when taken in excess of 200–400 mg in adults and 20–40 mg in children. Toxicity may lead number of neuro-metabolic disorders due to anticholinesterase activity and also cause cell membrane disturbance ultimately affecting the digestion and metabolism.
Branch number is a key yield-related quantitative trait that directly afects the number of pods and seeds per soybean plant. In this study, an integrated approach with a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and haplotype and candidate gene analyses was used to determine the detailed genetic basis of branch number across a diverse set of soybean accessions. The GWAS revealed a total of eleven SNPs signifcantly associated with branch number across three environments using the fve GWAS models.
Pyramiding BPH genes in rice maintains resistance against the brown planthopper under climate change
Nilaparvata lugens (brown planthopper; BPH) is a significant rice pest in Asia, causing substantial yield losses. Pyramiding BPH resistance genes with diverse resistance traits into rice cultivars is an effective strategy for pest management. However, the response of pyramiding combinations to environmental changes remains unclear. To address this knowledge gap, we investigated three pyramiding rice lines (BPH2 + 32, BPH9 + 32, and BPH18 + 32) in the context of varying climate change conditions, ensuring sufficient N. lugens-rice interactions.
Maize ear length has garnered considerable attention due to its high correlation with yield. In this study, six maize inbred lines of significant importance in maize breeding were used as parents. The temperate maize inbred line Ye107, characterized by a short ear, was crossed with five tropical or subtropical inbred lines featuring longer ears, creating a multi-parent population displaying significant variations in ear length. Through genome-wide association studies and mutation analysis, the A/G variation at SNP_183573532 on chromosome 3 was identified as an effective site for discriminating long-ear maize. Furthermore, the associated gene Zm00001d042906 was found to correlate with maize ear length.
Softening is a key factor affecting the quality and shelf life of fleshy fruits and is regulated by transcription factors (TFs). Our previous studies have shown that knockout of the NOR-like1 gene, a NAC transcription factor, can affect fruit ripening and firmness, but the molecular of NOR-like1 regulating fruit softening is not fully understand. Here, we firstly generate the NOR-like1 over-expressing lines (OE-NOR-like1),
Sweet potato is grown in tropical countries for its edible tubers, which have become an essential food source. It is usually propagated through vine-cutting, which can be obtained from harvested plants or nurseries intended for cutting production only. The recurrent use of vines may cause increased weevil infestation. The crop is known to be infested with insect pests.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have emerged as a powerful tool for unraveling intricate genotype-phenotype association across various species. Maize (Zea mays L.), renowned for its extensive genetic diversity and rapid linkage disequilibrium (LD), stands as an exemplary candidate for GWAS. In maize, GWAS has made significant advancements by pinpointing numerous genetic loci and potential genes associated with complex traits, including responses to both abiotic and biotic stress
Tomato necrotic ringspot virus (TNRV) was first reported in Thailand in 2011, where it continues to reduce the yield and quality of pepper and tomato crops. Here, we report the complete genome sequence of TNRV isolate chilli-CR derived from next-generation sequencing. The TNRV genome comprises 16,595 nucleotides (nt) on three RNA segments. The L RNA is 8,858 nt, the M RNA is 4,724 nt, and the S RNA is 3,013 nt in length.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :