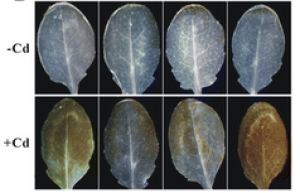
Non-essential trance metal such as cadmium (Cd) is toxic to plants. Although some plants have developed elaborate strategies to deal with absorbed Cd through multiple pathways, the regulatory mechanisms behind the Cd tolerance are not fully understood. Ferrochelatase-1 (FC1, EC4.99.1.1) is the terminal enzyme of heme biosynthesis, catalyzing insertion of ferrous ion into protoporphyrin IX. Recent studies have shown that FC1 is involved in several physiological processes.
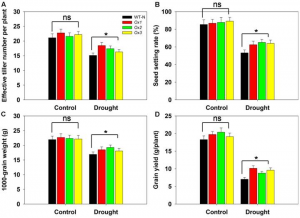
Drought is one of the environmental factors that severely restrict plant distribution and crop production. Recently, we reported that the high-affinity potassium transporter OsHAK1 plays important roles in K acquisition and translocation in rice over low and high K concentration ranges, however, knowledge on the regulatory roles of OsHAK1 in osmotic/drought stress is limited.
Kochia (Kochia scoparia L.), Russian thistle (Salsolatragus L.), and prickly lettuce (Lactuca serriola L.) are economically important weeds infesting dryland wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production systems in the western United States. Those weeds produce most of their seeds post-harvest. The objectives of this study were to determine the ability of an optical sensor, installed for on-the-go measurement of grain protein concentration, to detect the presence of green plant matter in flowing grain and assess the potential usefulness of this information for mapping weeds at harvest.
Northern corn leaf blight (NCLB), the most devastating leaf pathogen in maize (Zea mays L.), is caused by the heterothallic ascomycete Setosphaeria turcica. The pathogen population shows an extremely high genetic diversity in tropical and subtropical regions. Varietal resistance is the most efficient technique to control NCLB. Host resistance can be qualitative based on race-specific Ht genes or quantitative controlled by many genes with small effects. Quantitative resistance is moderately to highly effective and should be more durable combatting all races of the pathogen.
Soybean is the most important legume crop in the world. Several diseases in soybean lead to serious yield losses in major soybean-producing countries. Moreover, soybean can be infected by diverse viruses. Recently, we carried out a large-scale screening to identify viruses infecting soybean using available soybean transcriptome data. Of the screened transcriptomes, a soybean transcriptome for soybean seed development analysis contains several virus-associated sequences.
Fusarium fujikuroi causes bakanae ("foolish seedling") disease of rice which is characterized by hyper-elongation of seedlings resulting from production of gibberellic acids (GAs) by the fungus. This plant pathogen is also known for production of harmful mycotoxins, such as fusarins, fusaric acid, apicidin F and beauvericin. Recently, we generated the first de novo genome sequence of F. fujikuroi strain IMI 58289 combined with extensive transcriptional, epigenetic, proteomic and chemical product analyses.
Cassava, Manihot esculenta Crantz, has been positioned as one of the most promising crops world-wide representing the staple security for more than one billion people mainly in poor countries. Cassava production is constantly threatened by several diseases, including cassava bacterial blight (CBB) caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis (Xam), it is the most destructive disease causing heavy yield losses.
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is widely prevalent and causes Bacterial Leaf Blight (BLB) in Basmati rice grown in different areas of Pakistan. There is a need to use environmentally safe approaches to overcome the loss of grain yield in rice due to this disease. The present study aimed to develop inocula, based on native antagonistic bacteria for biocontrol of BLB and to increase the yield of Super Basmati rice variety.
Bacterial genomes are extremely diverse in size and composition. Biologists have long sought to explain such variability based on present-day selective and mutational forces. However, mutation rates can change dramatically over time, and experiments with hypermutable bacteria show that their genomes rapidly decay when propagated under the near absence of selection. Whether selection can prevent this decay is unclear.
Chondrodystrophy, characterized by short limbs and intervertebral disc disease (IVDD), is a common phenotype in many of the most popular dog breeds, including the dachshund, beagle, and French bulldog. Here, we report the identification of a FGF4 retrogene insertion on chromosome 12, the second FGF4 retrogene reported in the dog, as responsible for chondrodystrophy and IVDD. Identification of the causative mutation for IVDD will impact an incredibly large proportion of the dog population and provides a model for IVDD in humans, as FGF-associated mutations are responsible for IVDD and short stature in human achondroplasia.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :