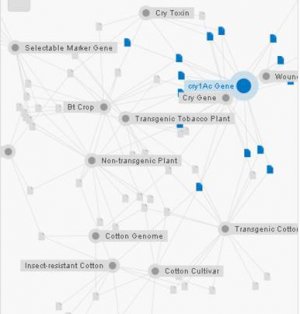
Most of the commercialized Bt crops express cry genes under 35S promoter that induces strong gene expression in all plant parts. However, targeted foreign gene expression in plants is esteemed more important as public may be likely to accept ‘less intrusive’ expression of transgene. We developed plant expression constructs harboring cry1Ac gene under control of wound-inducible promoter (AoPR1) to confine Bt gene expression in insect wounding parts of the plants in comparison with cry1Ac gene under the control of 35S promoter.
OsSRT1 is a NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase, closely related to the human SIRT6 that plays key roles in genome stability and metabolic homeostasis. In this work, we investigated the role of OsSRT1 in rice seed development. Down-regulation of OsSRT1 induced higher expression of Rice Starch Regulator1 (RSR1) and amylases genes in developing seeds
Signaling pathways responsive to both external and internal signals are essential for implementation of biological functions in a cell. After perceiving the signal, the signaling needs to be attenuated and terminated, usually mediated by the endocytic trafficking, to ensure a temporal and spatial control of the signaling activities. In mammals, disruption of the vacuolar protein sorting 41 (VPS41)-mediated endocytic pathway was reported to cause pleiotropic diseases such as neurological disorders.
The recent Paris accord on global climate change is a key step in acknowledging biophysical limits to human actions, but the challenge of respecting the biosphere’s ecological limits remains underrated. We analyze how respecting these limits squarely conflicts with an economy centered on growth and technology to mitigate environmental stress. The need to mitigate human impacts on species and natural systems has made conservation science a major multidisciplinary discipline. Society and conservation science have tried unsuccessfully to resolve this need within the growth paradigm.
Rice produces low-molecular-weight antimicrobial compounds known as phytoalexins, in response to not only pathogen attack but also abiotic stresses including ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Rice phytoalexins are composed of diterpenoids and a flavonoid. Recent studies have indicated that endogenous jasmonyl-l-isoleucine (JA-Ile) is not necessarily required for the production of diterpenoid phytoalexins in blast-infected or CuCl2-treated rice leaves.
The maize genome, similar to those of most plant genomes, is 98% noncoding. Much of the remainder is a vast desert of repeats that remain repressed throughout the cell cycle. The plant cell orchestrates its complex activities by restricting access to functional regions with an open chromatin configuration. Here, we identify the small portion (<1%) of the maize genome residing in open chromatin.
Low phosphorus (P) tolerance in rice is a biologically and agronomically important character. Low P tolerant Indica -type rice genotypes, Sahbhagi Dhan (SD) and Chakhao Poreiton (CP), are adapted to acidic soils and show variable response to low P levels. Using RNAseq approach, transcriptome data was generated from roots of SD and CP after 15 days of low P treatment to understand differences and similarities at molecular level.
Disease resistance is an important goal of crop improvement. The molecular mechanism of resistance requires further study. Here, we report the identification of a rice leaf color mutant, lc7, which is defective in chlorophyll synthesis and photosynthesis but confers resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Map-based cloning revealed that lc7 encodes a mutant ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase1 (Fd-GOGAT1)
Development of rice genotypes tolerant to complete submergence in the Mekong Delta was carried out for three continuous years by CLUES Project fund. Eighty five high-yielding cultivars and eighty four progenies from backcrossing population (BC3F3) of OM1490/IR64 Sub1 were used to study the yield components and submergence tolerance. Phenotyping was implemented at three stages: seedling, tillering and heading.
The circadian clock regulates biochemical, physiological, endocrine, and behavioral features of higher organisms. Although the timekeeping mechanism and many of the functions it governs rely on transcriptional regulation, posttranscriptional regulation also plays an important role. We show here that levels of the abundant Drosophila microRNA mir-276a oscillate under 24-h light–dark cycles and are regulated by the transcription factor Chorion factor 2


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :