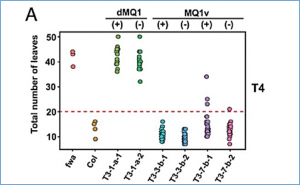
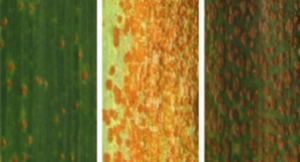
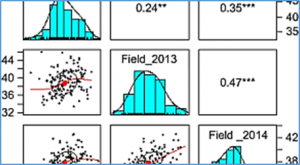
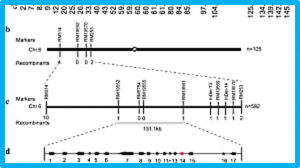
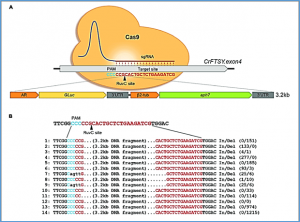
CRISPR-based targeted modification of epigenetic marks such as DNA cytosine methylation is an important strategy to regulate the expression of genes and their associated phenotypes. Although plants have DNA methylation in all sequence contexts (CG, CHG, CHH, where H = A, T, C), methylation in the symmetric CG context is particularly important for gene silencing and is very efficiently maintained through mitotic and meiotic cell divisions
The wheat landrace Hongmazha (HMZ) possesses adult plant resistance (APR) to leaf rust. To detect and validate quantitative trait locus (QTL) for the APR, four wheat populations were assessed for leaf rust severity in a total of eight field and greenhouse experiments. The mapping population Aquileja × HMZ (120 recombinant inbred lines, RILs) was genotyped using 90 K SNP markers. A major QTL (QLr.cau-2BL) was detected between the markers IWB3854 and IWB21922 on chromosome 2BL
Sucrose synthase (SUS), a key enzyme of the sucrose metabolism pathway, is encoded by a multi-gene family in plants. To date, dozens of SUS gene families have been characterized in various plant genomes. However, only a few studies have performed comprehensive analyses in tropical crops like cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). In the present study, seven non-redundant members of the SUS gene family (MeSUS1-7) were identified and characterized from the cassava genome.
One of the breeding goals in rapeseed production is to enhance the seed oil content to cater to the increased demand for vegetable oils due to a growing global population. To investigate the genetic basis of variation in seed oil content, we used 60 K Brassica Infinium SNP array along with phenotype data of 203 Chinese semi-winter rapeseed accessions to perform a genome-wide analysis of haplotype blocks associated with the oil content.
Accumulation of anthocyanin is a desirable trait to be selected in rice domestication, but the molecular mechanism of anthocyanin biosynthesis in rice remains largely unknown. In this study, a novel allele of chromogen gene C, OrC1, from Oryza rufipongon was cloned and identified as a determinant regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Although OrC1 functions in purple apiculus, leaf sheath and stigma in indica background, it only promotes purple apiculus in japonica
Genetically modified yellow corn has increasingly been used in the Philippines since 2002. In just a period of 17 years, the area planted increased to about 835 thousand hectares, increasing by an average of 31.24% per year. A third of all corn farmers in the Philippines or about 460 thousand families are planting GM corn. Total factor productivity growth in the corn industry of the country was estimated to be 11.45% higher due to GM corn adoption.
The nitrate transporter NRT2.1, which plays a central role in high-affinity nitrate uptake in roots, is activated at the post-translational level in response to nitrogen (N) starvation1,2. However, the critical enzymes required for the post-translational activation of NRT2.1 remain to be identified. Here, we show that a type 2C protein phosphatase, designated CEPD-induced phosphatase (CEPH), activates high-affinity nitrate uptake by directly dephosphorylating Ser501 of NRT2.1, a residue that functions as a negative phospho-switch in Arabidopsis2.
Conventional methods of DNA sequence insertion into plants, using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation or microprojectile bombardment, result in the integration of the DNA at random sites in the genome. These plants may exhibit altered agronomic traits as a consequence of disruption or silencing of genes that serve a critical function. Also, genes of interest inserted at random sites are often not expressed at the desired level.
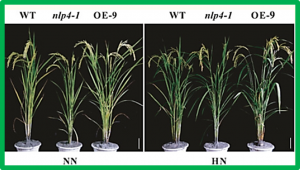
Nitrogen (N) is one of the key essential macronutrients that affects rice growth and yield. Inorganic N fertilizers are excessively used to boost yield and generate serious collateral environmental pollution. Therefore, improving crop N use efficiency (NUE) is highly desirable and has been a major endeavour in crop improvement. However, only a few regulators have been identified that can be used to improve NUE in rice to date.
Genomic selection (GS) has the potential to increase the rate of genetic gain in sugarcane beyond the levels achieved by conventional phenotypic selection (PS). To assess different implementation strategies, we simulated two different GS-based breeding strategies and compared genetic gain and genetic variance over five breeding cycles to standard PS. GS scheme 1 followed similar routines like conventional PS but included three rapid recurrent genomic selection (RRGS) steps.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :