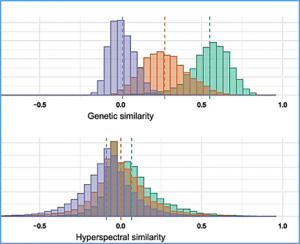
Wild relatives or progenitors of crops are important resources for breeding and for understanding domestication. Identifying them, however, is difficult because of extinction, hybridization, and the challenge of distinguishing them from feral forms. Here, we use collection-based systematics, iconography, and resequenced accessions of Citrullus lanatus and other species of Citrullus to search for the potential progenitor of the domesticated watermelon.
Salinity is a major environmental factor limiting crop growth and productivity. The root is the first plant organ to encounter salt stress, yet the effects of salinity on maize root development remain unclear. In this study, the natural variations in 14 root and 4 shoot traits were evaluated in 319 maize inbred lines under control and saline conditions. Considerable phenotypic variations were observed for all traits, with high salt concentrations decreasing the root length, but increasing the root diameter.
The maturation of green fleshy fruit to become colourful and flavoursome is an important strategy for plant reproduction and dispersal. In tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and many other species, fruit ripening is intimately linked to the biogenesis of chromoplasts, the plastids that are abundant in ripe fruit and specialized for the accumulation of carotenoid pigments. Chromoplasts develop from pre-existing chloroplasts in the fruit, but the mechanisms underlying this transition are poorly understood. Here, we reveal a role for the chloroplast-associated protein degradation (CHLORAD) proteolytic pathway in chromoplast differentiation.
Understanding and identifying improved adaptation to abiotic stresses such as heat stress has been the focus of a number of studies in recent decades. However, confusing and potentially misleading terminology has made progress difficult and hard to apply within breeding programs selecting for improved adaption to heat stress conditions. This study proposes that adaption to heat stress (and other abiotic stresses) be considered as the combination of total performance and responsiveness to heat stress.
Temperate maize (Zea mays L.) breeding programs often rely on limited genetic diversity, which can be expanded by incorporating exotic germplasm. The aims of this study were to perform characterization of inbred lines derived from the tropical BS39 population using different breeding methods, to identify genomic regions showing segregation distortion in lines derived by the DH process using spontaneous haploid genome doubling (SHGD)
The demand for sustainable sources of biomass is increasing worldwide. The early prediction of biomass via indirect selection of dry matter yield (DMY) based on hyperspectral and/or genomic prediction is crucial to affordably untap the potential of winter rye (Secale cereale L.) as a dual-purpose crop. However, this estimation involves multiple genetic backgrounds and genetic relatedness is a crucial factor in genomic selection (GS).
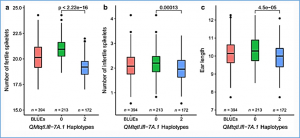
Grain yield in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a polygenic trait representing the culmination of many developmental processes and their interactions with the environment. Toward maintaining genetic gains in yield potential, ‘reductionist approaches’ are commonly undertaken by which the genetic control of yield components, that collectively determine yield, are established. Here we use an eight-founder German multi-parental wheat population to investigate the genetic control and phenotypic trade-offs between 15 yield components.
Sugarcane breeding programs have achieved up to 1% genetic gain in key traits such as tonnes of cane per hectare (TCH), commercial cane sugar (CCS) and Fibre content over the past decades. Here, we assess the potential of genomic selection to increase the rate of genetic gain for these traits by deriving genomic estimated breeding values (GEBVs) from a reference population of 3984 clones genotyped for 26 K SNP. We evaluated the three different genomic prediction approaches GBLUP, genomic single step (GenomicSS), and BayesR.
Autophagy is a highly conserved catabolic process regulating cellular homeostasis and adaptation to different biotic and abiotic stress. Several autophagy-related proteins (ATGs) are reported to be involved in autophagic processes, and considering their importance in regulating growth and stress adaptation, these proteins have been identified and characterized in several plant species. However, there is no information available on the role of autophagy-related proteins regulating the tolerance of tomato to tomato leaf curl disease (ToLCD).
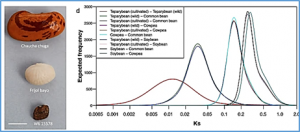
Tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolis A. Gray), native to the Sonoran Desert, is highly adapted to heat and drought. It is a sister species of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), the most important legume protein source for direct human consumption, and whose production is threatened by climate change. Here, we report on the tepary genome including exploration of possible mechanisms for resilience to moderate heat stress and a reduced disease resistance gene repertoire, consistent with adaptation to arid and hot environments.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :