Modern plant breeding heavily relies on the use of molecular markers. In recent years, next generation sequencing (NGS) emerged as a powerful technology to discover DNA sequence polymorphisms and generate molecular markers very rapidly and cost effectively, accelerating the plant breeding programmes. A single dominant locus, Frl, in tomato provides resistance to the fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici (FORL),
Rose, one of the world’s most-loved and commercially important ornamental plants, is predominantly tetraploid, possessing four rather than two copies of each chromosome. This condition complicates genetic analysis, and so the majority of previous genetic studies in rose have been performed at the diploid level. However, there may be advantages to performing genetic analyses at the tetraploid level, not least because this is the ploidy level of most breeding germplasm.
An indigenous maize landrace from the Sierra Mixe region of Oaxaca, Mexico exhibits extensive formation of aerial roots which exude large volumes of a polysaccharide-rich gel matrix or "mucilage" that harbors diazotrophic microbiota. We hypothesize that the mucilage associated microbial community carries out multiple functions, including disassembly of the mucilage polysaccharide. In situ, hydrolytic assay of the mucilage revealed endogenous arabinofuranosidase, galactosidase, fucosidase, mannosidase and xylanase activities
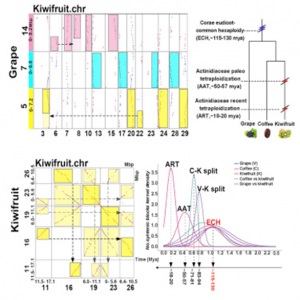
The genome of kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) was sequenced previously, the first in the Actinidiaceae family. It was shown to have been affected by polyploidization events, the nature of which has been elusive. Here, we performed a reanalysis of the genome and found clear evidence of 2 tetraploidization events, with one occurring ∼50–57 million years ago (Mya) and the other ∼18–20 Mya. Two subgenomes produced by each event have been under balanced fractionation.
Lesion mimic mutants (LMMs) commonly exhibit spontaneous cell death similar to the hypersensitive defense response that occurs in plants in response to pathogen infection. Several lesion mimic mutants have been isolated and characterized, but their molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown. Here, a spotted leaf sheath (sles) mutant derived from japonica cultivar Koshihikari is described. The sles phenotype differed from that of other LMMs in that lesion mimic spots were observed on the leaf sheath rather than on leaves.
This study evaluates optimal cross selection to balance selection and maintenance of genetic diversity in two-part plant breeding programs with rapid recurrent genomic selection. The two-part program reorganises a conventional breeding program into a population improvement component with recurrent genomic selection to increase the mean value of germplasm and a product development component with standard methods to develop new lines.
Maize starch plays a critical role in food processing and industrial application. The pasting properties, the most important starch characteristics, have enormous influence on fabrication property, flavor characteristics, storage, cooking, and baking. Understanding the genetic basis of starch pasting properties will be beneficial for manipulation of starch properties for a given purpose. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are becoming a powerful tool for dissecting the complex traits.
Genic male-sterile line is an efficient tool for commercial hybrid seed production in pepper; however, so far, only few genes controlling this trait have been cloned. A spontaneous genic male-sterile mutant, msc-1, had been identified and widely used in China, of which the male-sterile trait was proved to be controlled by a single recessive locus. For cloning the gene(s) underlying the msc-1 locus, genome resequencing and comparison analyses were performed between male-sterile and male-fertile lines.
Genome-Wide Association Studies of Photosynthetic Traits Related to Phosphorus Efficiency in Soybean
Photosynthesis is the basis of plant growth and development, and is seriously affected by low phosphorus (P) stress. However, few studies have reported for the genetic foundation of photosynthetic response to low P stress in soybean. To address this issue, 219 soybeanaccessions were genotyped by 292,035 high-quality single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and phenotyped under normal and low P conditions in 2015 and 2016. These datasets were used to identify quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) for photosynthesis-related traits using mrMLM, ISIS EM-BLASSO, pLARmEB, FASTmrMLM, FASTmrEMMA, and pKWmEB methods.
Efficient removal of bio-refractory dissolved organic matter (DOM) and colorants is essential for discharging or reusing the distillery wastewater. An important part of recalcitrant DOM still exists in the effluent of regular coagulation though the ferric coagulant has been found to be effective in decoloration. The present work adopted powdered activated carbon (PAC) as ballasting agent to achieve robust separation effect and efficiency of bio-refractory DOM from the bio-chemically treated cassava distillery wastewater (BTDWW).


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :