Lignocellulosic biomass is a potential major resource for renewable energy production. Plant cell-wall deconstruction, however, remains an inefficient process, mainly due to the recalcitrant nature of the lignin and cellulosic components, that requires chemical pretreatment methods prior to degradation. This study aims to overcome this barrier by combining two paradigms into a single system, by using a synthetic biology approach.
A high-salt environment represents environmental stress for most plants. Those that can grow and thrive in such an environment must have membrane transport systems that can respond effectively. Plant roots absorb Na+ from the soil, and the plant must maintain Na+ homeostasis to survive salt stress. A major mechanism by which salt-tolerant plants adapt to salt stress is through modulation of ion transport genes.
The 70-kD heat shock proteins (Hsp70s) are highly conserved molecular chaperones that play essential roles in cellular processes including abiotic stress responses. Physcomitrella patens serves as a representative of the first terrestrial plants and can recover from serious dehydration. To assess the possible relationship between P. patens Hsp70s and dehydration tolerance, we analyzed the P. patens genome and found at least 21 genes encoding Hsp70s.
Nutritional quality and yield are equally important considerations in crop breeding, although they sometimes appear at odds. In this work we made the discovery that these traits are linked through regulation by two transcription factors. Mutations that affect the expression of these transcription factors can improve the nutritional quality of the seed but also can reduce kernel yield and hardness. Therefore future corn-breeding programs should silence zein genes directly, not by blocking transcription factors.
Although auxin oxidation has long been known to be the primary mechanism of auxin catabolism and Arabidopsis seedlings have 10–100 more 2-oxindole 3-acetic acid compared with other auxin catabolic products, the enzymes that constitutively catalyze this process remained unknown. This work fills the gap by identifying and characterizing the Arabidopsis proteins DIOXYGENASE FOR AUXIN OXIDATION 1 (DAO1) and DAO2
Southern root-knot nematode (RKN, Meloidogyne incognita) is a serious pest of cultivated watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var. lanatus) in southern regions of the United States and no resistance is known to exist in commercial watermelon cultivars. Wild watermelon relatives (Citrullus lanatus var. citroides) have been shown in greenhouse studies to possess varying degrees of resistance to RKN species. Experiments were conducted over 2 yr to assess resistance of southern RKN in C. lanatus var. citroides accessions from the U.S.
Rice bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is one of the most destructive rice diseases worldwide. Therefore, in addition to breeding disease-resistant rice cultivars, it is desirable to develop effective biocontrol agents against Xoo. Here, we report that a soil bacterium Pseudomonas taiwanensis displayed strong antagonistic activity against Xoo. Using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry, we identified an iron chelator, pyoverdine, secreted by P. taiwanensis that could inhibit the growth of Xoo.
MicroRNAs are important regulators of gene expression in unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes. They are generally embedded in stem–loops of precursor transcripts and are excised by the dsRNA-specific nuclease DICER with the assistance of dsRNA-binding proteins. In animals and plants, proteins harboring two or three dsRNA-binding domains (dsRBDs) are involved in microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis.
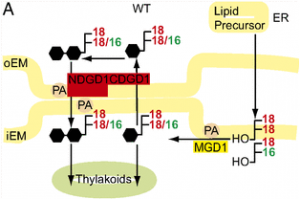
Establishment of the progenitor of chloroplasts by the host plant cell during endosymbiosis required the integration of two sets of biological membranes, the endoplasmic reticulum and the chloroplast envelopes, participating in the synthesis of galactolipid precursors for the photosynthetic membranes. Galactolipid synthesis is unequally distributed between the two envelope membranes, necessitating lipid transfer between the envelopes and toward the thylakoids.
Proper timing of flowering transition is vital for the reproductive success of plants and orchestrated by endogenous and external factors; however, the mechanisms of how plants regulate flowering under high light are not well understood. In this study, we show that promotion of flowering by high light involves the coupling of chloroplast retrograde signals and transcriptional silencing of the floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC).


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :