DNA methylation is critical for transposon silencing and gene regulation. DNA methylation levels are determined by the combined activities of DNA methyltransferases and demethylases. This study found a 39-bp DNA methylation monitoring sequence (MEMS) in the promoter of the DNA demethylase REPRESSOR OF SILENCING 1 (ROS1) gene of Arabidopsis plants. DNA methylation of MEMS is responsive to both RNA-directed DNA methylation and ROS1-dependent active demethylation.
The present work extends redox-based change in enzyme activity to the TCA cycle of plant mitochondria. Thioredoxin (TRX) was found to regulate the activity of enzymes of the mitochondrial cycle (succinate dehydrogenase and fumarase) and of an enzyme associated with it (ATP-citrate lyase) by modulating thiol redox status. A combination of experiments based on mutant and carbon isotope labeling analyses provides evidence that flux through this pathway is coordinately modulated by TRX at the enzyme level of both mitochondria and cytosol.
The centromere is the part of the chromosome that is involved with movement in mitosis and meiosis. The activity of the centromere is epigenetic in that the underlying DNA sequences do not necessarily determine function. In the present study, a chromosomal fragment was followed in which a sequential de novo formation and inactivation occurred for the position of the active centromere.
Striga hermonthica (Del.) Benth. and Striga asiatica (L.) Kuntze severely affect maize (Zea mays L.) production in sub-Saharan Africa. A single Striga plant produces a large number of seeds that form a bank of viable but dormant seed in the soil until they get a chemical signal from suitable maize host roots. Imidazolinone-resistant (IR) open-pollinated maize varieties (OPVs) developed for Striga control were tested in diverse environments in four countries of eastern Africa in 2004.
The distribution of fitness effects of new mutations (the DFE) is a key parameter in determining the course of evolution. This fact has motivated extensive efforts to measure the DFE or to predict it from first principles. However, just as the DFE determines the course of evolution, the evolutionary process itself constrains the DFE. Here, we analyze a simple model of genome evolution in a constant environment in which natural selection drives the population toward a dynamic steady state where beneficial and deleterious substitutions balance.
Block designs are normally used in evaluation of crop varieties. The responses or yield data arising from designed trials in a crop variety improvement program are generally analyzed using linear mixed models under the frequentist paradigm. Such analysis ignores information on the genotypic parameters available from previous similar trials. Another approach with a relatively wider inferential framework is Bayesian, which integrates the prior information with the likelihood of current data.
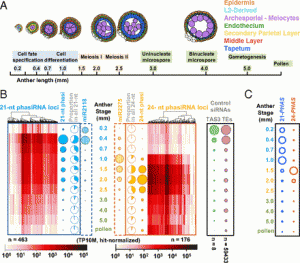
By RNA profiling of 10 stages of maize anthers plus mature pollen, we found two distinct classes of phased small-interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs): 21-nt premeiotic phasiRNAs, after germinal and somatic cell specification, and 24-nt meiotic phasiRNAs coordinately accumulated during meiosis and persist into pollen. Sequencing of RNA from five male-sterile, anther developmental mutants—ocl4, mac1, ms23, msca1, and ameiotic1—demonstrated the involvement of specific somatic layers.
Perennial plants display seasonal cycles of growth. For example, in the trees of boreal temperate forests, growth must cease prior to the advent of winter and cold hardiness must be acquired to survive extreme low temperature. Growth cessation and activation of transcriptional programs underlying adaptive responses associated with cold hardiness are photoperiodically controlled. We show that the evolutionarily conserved protein FD implicated in the control of flowering mediates photoperiodic control of seasonal growth in trees by forming a complex with FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) protein.
Plant growth requires a balanced supply of mineral nutrients. However, the availability of minerals varies constantly in the environment. How do plants adapt to low or high levels of minerals in the soil? The answer to this question holds the key to sustainable crop production. Mg is an essential macronutrient for plants, but high levels of Mg2+ can become toxic. This study uncovered a regulatory mechanism, consisting of two calcineurin B-like (CBL)
Earlier soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] planting, increased seed costs, and higher commodity prices have led to a surge in the use of soybean fungicide and insecticide seed treatments, while recent studies have suggested that growers should consider lowering seeding rates to increase their return on investment. Ultimately, growers would like to know the value proposition of combining seed treatments with lowered seeding rates. Therefore, three seed treatments (untreated, ApronMaxx, and CruiserMaxx) and six seeding rates (98,800, 148,200, 197,600, 247,000, 296,400, and 345,800 seeds ha−1)


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :