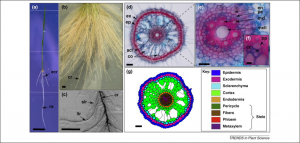
Plant roots function as an interface between plants and the complex soil environment. Root systems of higher plants consist of different root types (RTs) that maximize their adaptive potential in heterogenous soil for nutrient uptake and anchorage. This study pioneers the molecular examination of individual RTs of adult rice root systems. The global signature of the transcriptional activity of each RT reveals significant quantitative and qualitative differences that predict functional diversity and specialization.
Bird feeding is essentially a massive global supplementary feeding experiment, yet few studies have attempted to explore its ecological effects. In this study we use an in situ experimental approach to investigate the impacts of bird feeding on the structure of local bird assemblages. We present vital evidence that bird feeding contributes to the bird community patterns we observe in urban areas. In particular, the study demonstrates that common feeding practices can encourage higher densities of introduced birds, with potential negative consequences for native birds.
The rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae is a serious pathogen that jeopardises the world's most important food-security crop. Ten common Malaysian rice varieties were examined for their morphological, physiological and genomic responses to this rice blast pathogen. qPCR quantification was used to assess the growth of the pathogen population in resistant and susceptible rice varieties. The chlorophyll content and photosynthesis were also measured to further understand the disruptive effects that M. oryzae has on infected plants of these varieties.
Common blight [caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli Smith (Dye)] is a major bacterial disease causing >40% seed yield and quality losses in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) worldwide. Use of resistant cultivars is crucial for its effective, economical, and environment friendly integrated management and control. Common blight resistant germplasm are found in the primary, secondary, and tertiary gene pools of the common bean. Substantial progress has been made in understanding the pathogenic variation, germplasm screening methods
The growing global population and shrinking arable land area require efficient plant breeding. Novel strategies assisted by certain markers have proven effective for genetic gains. Fortunately, cutting-edge sequencing technologies bring us a deluge of genomes and genetic variations, enlightening the potential of marker development. However, a large gap still exists between the potential of molecular markers and actual plant breeding practices.
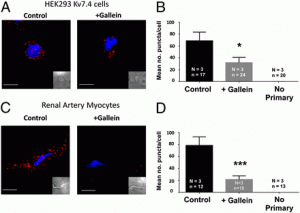
The Kv7.4 potassium channel is a critical regulator of vascular contractility both at rest and as a functional endpoint for a number of endogenous vasodilators. Despite its key role, nothing is known about the processes that determine Kv7.4 channel activity. We reveal an interaction between G-protein βγ subunits and Kv7.4 that is crucial for channel responses to membrane voltage. Blocking this interaction ablates channel activity, prevents β-adrenoceptor–mediated relaxation, and constricts renal arteries.
A fundamental dilemma in ecology is to reconcile the degree to which ecological processes are generalizable among taxa and ecosystems or determined primarily by taxonomic identity. We apply a unique dataset of organisms from a diverse marine community to test the applicability of two theories, metabolic theory of ecology (MTE) and ecological stoichiometry (EST), and the role of taxonomic identity for predicting nutrient excretion rates by fishes and macroinvertebrates.
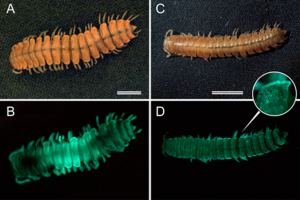
The enigmatic millipede Xystocheir bistipita has been rediscovered after a half-century. The rediscovery unexpectedly reveals that the species is bioluminescent. By reconstructing its evolutionary history, we show that X. bistipita is the evolutionary sister of Motyxia, the only bioluminescent millipede genus in the order Polydesmida
Climate change causes several abiotic stresses in crops affecting their productivity. In a study led by researchers from Monash University, they discovered the gene responsible for plant growth during warmer temperatures.
The Muller F element (4.2 Mb, ~80 protein-coding genes) is an unusual autosome of Drosophila melanogaster; it is mostly heterochromatic with a low recombination rate. To investigate how these properties impact the evolution of repeats and genes, we manually improved the sequence and annotated the genes on the D. erecta, D. mojavensis, and D. grimshawi F elements and euchromatic domains from the Muller D element.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :