In vascular (Arabidopsis thaliana) and nonvascular (Physcomitrella patens) plants, PHOSPHATE 1 (PHO1) homologs play important roles in the acquisition and transfer of phosphate. The tomato genome contains six genes (SlPHO1;1-SlPHO1;6) homologous to AtPHO1. The six proteins have typical characteristics of the plant PHO1 family, such as the three SPX sub domains in the N-terminal portion and one EXS domain in the C-terminal portion.
We analyzed a segregating monoparental dihaploid potato population comprising 215 genotypes derived from a tetraploid variety that is highly resistant to Synchytrium endobioticum pathotypes 18 and 6. The clear bimodal segregation for both pathotypes indicated that a major dominant resistance factor in a simplex allele configuration was present in the tetraploid donor genotype. Compared to that in previous analyses of the same tetraploid donor in conventional crosses with susceptible tetraploid genotypes,
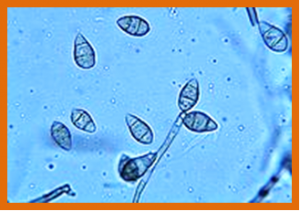
Three versatile QTL for soybean downy mildew resistance in Japan were detected using five RIL populations and confirmed using recombinant fixed pairs or a backcrossed line. Downy mildew reduces soybean seed quality and size. It is a problem in Japan, where 90% of soybean grown is used as food. In the USA, 33 downy mildew races have been reported, but race differentiation in Japan is unclear.
The plant genome encodes resistance (R) genes that are one of the major genomic resources to enhance disease resistance in various crops. R gene products, R proteins, serve as intracellular receptors for pathogen effectors, leading to activation of effector-triggered immunity. Due to the importance of R proteins, elucidation of their signaling pathways is an important research goal. We revealed that OsSPK1, a GDP/GTP exchange factor for the small GTPase OsRac1, is a direct binding protein of the rice R protein Pit, which is a resistance protein to rice blast fungus.
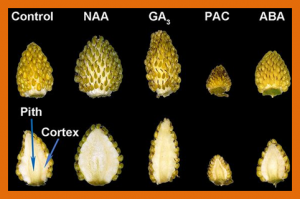
Using strawberry fruit as a model system, we uncover the mechanistic interactions between auxin, gibberellic acid (GA), and abscisic acid (ABA) that regulate the entire process of fruit development. Interlinked regulatory loops control ABA levels during fruit development. During the early stages, auxin/GA turns on a feedback loop to activate the removal of ABA via FveCYP707A4a-dependent catabolism needed for fruit growth.
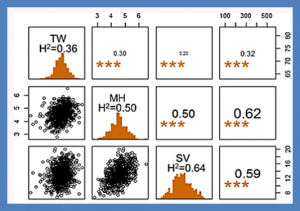
Multi-trait genomic prediction models can be used to predict labor-intensive or expensive correlated traits where phenotyping depth of correlated traits could be larger than phenotyping depth of targeted traits, reducing resources and improving prediction accuracy. This is particularly important in the context of allocating phenotyping resource in plant breeding programs. The objective of this work was to evaluate multi-trait models predictive ability with different depth of phenotypic information from correlated traits.
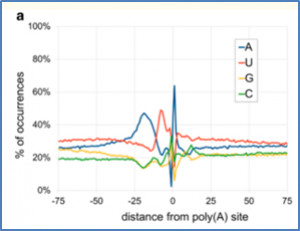
Polyadenylation plays an important role in gene regulation, thus affecting a wide variety of biological processes. In the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae the cleavage factor I protein Rpb35 is required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation and fungal virulence. Here we present the bioinformatic approach and output data related to a global survey of polyadenylation site usage in M. oryzae wild-type and Δrbp35 strains under a variety of nutrient conditions, some of which simulate the conditions experienced by the fungus during part of its infection cycle.
The western Mediterranean region provided the founder population of domesticated narrow-leafed lupin
The evolutionary history of plants during domestication profoundly shaped the genome structure and genetic diversity of today’s crops. Advances in next-generation sequencing technologies allow unprecedented opportunities to understand genome evolution in minor crops, which constitute the majority of plant domestications. A diverse set of 231 wild and domesticated narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) accessions were subjected to genotyping-by-sequencing using diversity arrays technology.
Polyadenylation plays an important role in gene regulation, thus affecting a wide variety of biological processes. In the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae the cleavage factor I protein Rpb35 is required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation and fungal virulence. Here we present the bioinformatic approach and output data related to a global survey of polyadenylation site usage in M.
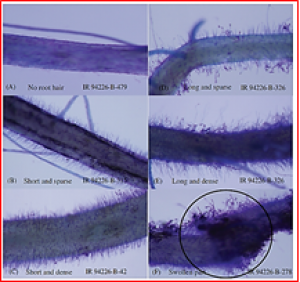
The development of rice varieties for dry direct-seeded conditions can be accelerated by selecting suitable traits. In the present investigation, traits hypothesized to be important for direct-seeded conditions in rainfed systems, including seedling emergence, early vegetative vigour, nutrient uptake, nodal root number, and root hair length and density, were characterized to study the genetic control of these traits and their relationship with grain yield under seedling- and reproductive-stage drought stress.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :