|
ASTRACT
Iron toxicity strongly influences He Thu rice yield under acid sulfate soils in Mekong Delta. Leaf bronzing is the typical symptom. Variety IR 50404 yielded the best when leaf iron content of 200 – 350 mg/kg. Its yield declined when leaf iron content of over 350 mg/kg and downed at 450 mg/kg.
Increasing Fe2+ in the medium enhanced leaf and tiller Fe accumulation. The rice plant was inhibited its nutrient uptake and became poor growth. Rice variety IR 50404 addressed its iron toxicity tolerance better than OM 5451.
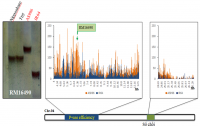
Water logging strongly decreased Eh, increased soil pH and ion Fe2+ in soil solution. The maximum Fe2+ in some soil samples come from acid sulfate soils in Mekong Delta varied from 196 ppm to 3,087 ppm. The peak of Fe2+ appeared from 14 to 42 days under water logging ngập nước. Non-significant difference of Fe2+ between potential and active acid sulfate soils.
There is a positive correlation between ion Fe2+ after water logging and iron styles in the soil (FeO, FeDCB, Fett, Feks, Fets) at the initial analysis, pH H2O and organic content. However, the factors contributed to the Fe2+ increasing with different outputs, which depended on water logging time. Iron components in sustained silicate clay (Feks) were considered not to contribute to ferrous-ferric conversion when water logging. Organic matter is the key factor to determine Fe2+ content at the seven-day after water logging. Iron style of poor crystal (FeO), soil pH exhibited the important role to determine Fe2+ at the seven day after waterlogging up to the final situation. The reduced cristal oxyhydroxides slowly get along as compared to informal iron oxyhydroxides and poorly crystal oxyhydroxides. Fett style only took place in the reducing process to significantly increase Fe2+ from 42 to 49 days after water logging.
The study has stimulated the function of Fe2+ measure in soil solution at 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49 days after water logging and maximum Fe2+ content in soil solution. Accordingly, the function of Fe2+ content at 7 days after logging includes the variate of soil organic content. The function of Fe2+ content at 14 – 35 day after water logging depended on the variables of FeO+ pH. The function at 42 – 49 days after water logging depended on FeO+ pH + Fett + max Fe (p < 0,01).
Under iron toxicity stress, P and Zn applications were recommended to increase the oxidation at the rice rhizosphere, to reduce Fe2+ at roots, to prevent from Fe2+ ion into the rice flux, to reduce the worse impact by iron toxicity, to improve rice yield.
Possibly, water management could be considered as changing toxic water in the canals by clean water to reduce the stress in He Thu season.
|
[ Tin tức liên quan ]___________________________________________________ -
Pham ho Hai. 2011. PhD Thesis Abstract, IAS, Vietnam Study on cassava peels as by-product to feed cattle ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Le Quang Tuyen. 2011. “Genetic analysis for the resistance to small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus Fallén) in two rice varieties”. PhD Thesis Abstract (e-mail: lequangtuyen71@yahoo.com). Sugarcane Research and Development Centre. ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Evaluation of quality genotypes of Oleiferous brassica under different sources and levels of nutrients and their residual effect on succeeding cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] (Nguyen Thi Quynh Thuan) ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Biochemical and crystallographic characterization of starch branching enzymes from the Oryza sativa L. seeds (Vu Thi Nhuan, 2008) ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Development of technology for production of value added b-carotene rich mango powder (Nguyen Van Phong, 2007) ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Sonic hedgehog supplementation of oocyte and embryo culture media enhances development of IVF porcine embryos ( Thứ năm, 10/11/2011 )
-
Vuong nam trung. 2011. Identification of apparent digestibility energy and amino acid requirements of yorkshire pig at large scale production ( Thứ năm, 02/02/2012 )
-
The role of silicon in surface charge characteristics, Phosphorus sorption capacity and aluminium toxicity Of variable charge soils Nguyễn Quang Chơn (Email: chon.nq@iasvn.org) IAS ( Thứ ba, 24/04/2012 )
-
Integration of farmers in the shrimp value chain in mekong river delta, Vietnam. PhD. Thesis: Hồ Thị Minh Hợp. 2012.(Académie universitaire wallonie-europe ; université de liège – gembloux agro-bio-tech).Email: mhop75@yahoo.com ( Thứ ba, 24/04/2012 )
-
Ha dinh Tuan. 2012. Etiology of sugarcane ratoon stunt disease in Southeast Vietnam and management. PhD Thesis. Nong Lam University. Vietnam. ( Thứ ba, 28/08/2012 )
-
Research and development of the upland rice in the cropping systems of Ea Sup district, Daklak province (PhD. Thesis. Dao Minh So, 2012. IAS, Email: so.dm@iasvn.org) ( Thứ sáu, 14/12/2012 )
-
Study on early, drought tolerance hybrid maize and cultivation practices in Southern Vietnam (PhD Thesis (2013), Trương Vĩnh Hải, Email: hai.tv@iasvn.org ) ( Thứ ba, 24/06/2014 )
-
DINH THI LAM. 2021. Studies on wild genetic resources to improve phosphorus deficiency tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). ( Thứ hai, 08/08/2022 )
-
Studying the growth, development capacities and technical measures to increase yields, qualities of some exotic orchid cultivars (Cattleya, Dendrobium, Oncidium) for Northern Vietnam (PhD. Thesis: Hoang Xuan Lam) ( Thứ sáu, 27/06/2014 )
-
Research on identifying new varieties and cultivated techniques protocols to improve productivity and economic efficiency in tomato cultivation in Red River Delta (PhD. Thesis. Dang Van Nien) ( Thứ sáu, 27/06/2014 )
-
Processed Organic Fertilizer Influences On Soil Fertility Properties And Short- Duration Crop Genotypes’ Productivity Under South-Eastern Grey Soil Conditions. (PhD Thesis. Hoang Van Tam. 2014. The Institute of Agricultural Research for Southern Vietnam) ( Thứ hai, 21/07/2014 )
-
Study on P releasing and adsorption in lowland areas of Southern Vietnam and silicate application to raise available P for rice (Oryza sativa L.). (PhD Thesis. TRAN THI TUONG LINH, Submitted in August 14, 2014) ( Thứ năm, 14/08/2014 )
-
Research and application of molecule markers in breeding salt-tolerant Bacthom 7 rice variety. ( PhD Thesis. Dong Thi Kim Cuc) ( Thứ năm, 06/11/2014 )
-
Study on biological characteristics and technology of spawn production, cultivation of the King oyster mushroom ((Pleurotus eryngii) and Yunzhi mushroom (Trametes versicolor) in Vietnam.( PhD. Thesis. Nguyen Thi Bich Thuy) ( Thứ năm, 06/11/2014 )
-
Studying on potassium balance for sugarcane in Lam Son sugarcane belt, Thanh Hoa province.( PhD. Thesis. Pham Thi Thanh Huong) ( Thứ năm, 06/11/2014 )
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :