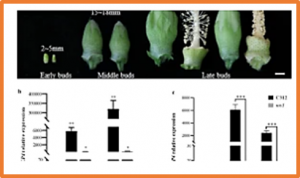
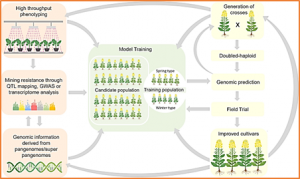
Utilization of heterosis is an important way to increase cotton yield and improve fiber quality in hybrid cotton development programs. Male sterility is used in the development of cotton hybrids to reduce the cost of hybrid seed production by eliminating the process of emasculation. From the transcriptome analysis of genic male sterile mutant (ms1) and its background C312 of G. hirsutum, a gene encoding germin-like protein (GhGLP4) was found significantly down-regulated in different developmental stages of ms1 anthers. To explore the gene function in cotton fertility, GhGLP4 was further studied and interfered by virus-induced gene silencing.
Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) is a notorious pest that threatens maize production worldwide. Current control measures involve the use of chemical insecticides and transgenic maize expressing Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxins. Although additional transgenes have confirmed insecticidal activity, limited research has been conducted in maize, at least partially due to the technical difficulty of maize transformation.
MYB transcription factors (TFs) have been reported to regulate the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, as well as to mediate plant adaption to abiotic stresses, including drought. However, the roles of MYB TFs in regulating plant architecture and yield potential remain poorly understood. Here, we studied the roles of the dehydration-inducible GmMYB14 gene in regulating plant architecture, high-density yield and drought tolerance through the brassinosteroid (BR) pathway in soybean.
The size and weight of edible organs have been strongly selected during crop domestication. Concurrently, human have also focused on nutritional and cultural characteristics of fruits and vegetables, at times countering selective pressures on beneficial size and weight alleles. Therefore, it is likely that novel improvement alleles for organ weight still segregate in ancestral germplasm. To date, five domestication and diversification genes affecting tomato fruit weight have been identified, yet the genetic basis for increases in weight has not been fully accounted for.
Micronutrients regulate the metabolic processes to ensure the normal functioning of the biological system in all living organisms. Micronutrient deficiency, thereby, can be detrimental that can result in serious health issues. Grains of graminaceous crops serve as an important source of micronutrients to the human population; however, the rise in hidden hunger and malnutrition indicates an insufficiency in meeting the nutritional requirements.
Brassica carinata [A.] Braun (BBCC, 2n = 34) is a climate-resilient oilseed. Its seed oil is high in erucic acid (> 40%), rendering it well suited for the production of biofuel and other bio-based applications. To enhance the competitiveness of B. carinata with high erucic B. napus (HEAR), lines with super-high erucic acid content were developed through interspecific hybridization. To this end, a fad2B null allele from Brassica juncea (AABB, 2n = 36) was introgressed into B. carinata, resulting in a B. carinata fad2B mutant with erucic acid levels of over 50%. Subsequently, the FAE allele from B. rapa spp. yellow sarson (AA, 2n = 20) was transferred to the fad2B B. carinata line, yielding lines with erucic acid contents of up to 57.9%.
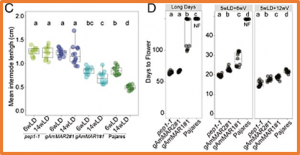
The timing of reproduction is an adaptive trait in many organisms. In plants, the timing, duration, and intensity of flowering differ between annual and perennial species. To identify interspecies variation in these traits, we studied introgression lines derived from hybridization of annual and perennial species, Arabis montbretiana and Arabis alpina, respectively. Recombination mapping identified two tandem A. montbretiana genes encoding MADS-domain transcription factors that confer extreme late flowering on A. alpina. These genes are related to the MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING (MAF) cluster of floral repressors of other Brassicaceae species and were named A. montbretiana (Am) MAF-RELATED (MAR) genes.
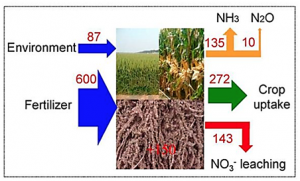
Hundreds of millions of smallholders in emerging countries substantially overuse nitrogen (N) fertilizers, driving local environmental pollution and global climate change. Despite local demonstration-scale successes, widespread mobilization of smallholders to adopt precise N management practices remains a challenge, largely due to associated high costs and complicated sampling and calculations. Here, we propose a long-term steady-state N balance (SSNB) approach without these complications that is suitable for sustainable smallholder farming. The hypothesis underpinning the concept of SSNB is that an intensively cultivated soil–crop system with excessive N inputs and high N losses can be transformed into a steady-state system with minimal losses while maintaining high yields.
Quantitative resistance (QR) has long been utilized to manage blackleg in Brassica napus (canola, oilseed rape), even before major resistance genes (R-genes) were extensively explored in breeding programmes. In contrast to R-gene-mediated qualitative resistance, QR reduces blackleg symptoms rather than completely eliminating the disease. As a polygenic trait, QR is controlled by numerous genes with modest effects, which exerts less pressure on the pathogen to evolve; hence, its effectiveness is more durable compared to R-gene-mediated resistance. Furthermore, combining QR with major R-genes has been shown to enhance resistance against diseases in important crops, including oilseed rape.
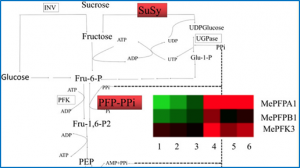
We identified 13 MePFK genes and characterised their sequence structure. The phylogenetic tree divided the 13 genes into two groups: nine were MePFKs and four were pyrophosphate-fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase (MePFPs). We confirmed by green fluorescent protein fusion protein expression that MePFK03 and MePFPA1 were localised in the chloroplast and cytoplasm, respectively.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :