Weeds are important biotic constraints to agricultural production, so herbicides are widely used with agronomic crops as the primary method of weed control. Accordingly, extensive efforts to develop herbicide-resistant (HR) crops have been made using various methods, including clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9)-mediated gene editing. Thus far, most of the HR crops developed using gene-editing methods have adopted site-specific mutations of endogenous genes, but rarely by insertion or deletion (indel) mutations.
Drought has become a major stress for agricultural productivity in temperate regions, such as central Europe. Thus, information on how crop plants respond to drought is important to develop tolerant hybrids and to ensure yield stability. Posttranscriptional regulation through changed protein abundances is an important mechanism of short-term response to stress events that has not yet been widely exploited in breeding strategies. Here, we investigated the response to repeated drought exposure of a tolerant and a sensitive maize hybrid in order to understand general protein abundance changes induced by singular drought or repeated drought events.
An exotic soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] accession, PI 567305, was reported to be highly resistant to three important nematode species, soybean cyst (SCN), root-knot (RKN), and reniform (RN) nematodes. However, genetic basis controlling broad-spectrum resistance in this germplasm has not been investigated. We report results of genetic analysis to identify genomic loci conferring resistance to these nematode species. A bi-parental population consisting of 242 F8-derived recombinant inbred lines (RILs) was developed from a cross of a nematode susceptible cultivar, Magellan, and resistant accession, PI 567305.
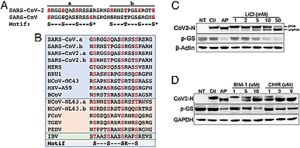
The coronaviruses responsible for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV), COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2), Middle East respiratory syndrome-CoV, and other coronavirus infections express a nucleocapsid protein (N) that is essential for viral replication, transcription, and virion assembly. Phosphorylation of N from SARS-CoV by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is required for its function and inhibition of GSK-3 with lithium impairs N phosphorylation, viral transcription, and replication. Here we report that the SARS-CoV-2 N protein contains GSK-3 consensus sequences and that this motif is conserved in diverse coronaviruses, raising the possibility that SARS-CoV-2 may be sensitive to GSK-3 inhibitors, including lithium.
The term “de-etiolation” refers to the light-dependent differentiation of etioplasts to chloroplasts in angiosperms. The underlying process involves reorganization of prolamellar bodies (PLBs) and prothylakoids into thylakoids, with concurrent changes in protein, lipid, and pigment composition, which together lead to the assembly of active photosynthetic complexes. Despite the highly conserved structure of PLBs among land plants, the processes that mediate PLB maintenance and their disassembly during de-etiolation are poorly understood. Among chloroplast thylakoid membrane–localized proteins, to date, only Curvature thylakoid 1 (CURT1) proteins were shown to exhibit intrinsic membrane-bending capacity.
Faba bean (Vicia faba L., 2n = 12) is an important food legume crop that is widely grown for multiple uses worldwide. However, no reference genome is currently available due to its very large genome size (approximately 13 Gb) and limited single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers as well as highly efficient genotyping tools have been reported for faba bean. In this study, 16.7 billion clean reads were obtained from transcriptome libraries of flowers and leaves of 102 global faba bean accessions
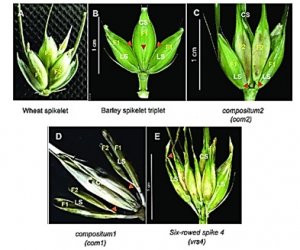
The genetic basis of cleistogamy (in which pollination occurs before the flower opens) in barley is centered on the Cleistogamy 1 locus (cly1). The sequence of the microRNA (miR172)-targeting site in the gene, which belongs to the APETALA2 family, differs between cleistogamous and chasmogamous cultivars at a single nucleotide position, resulting in the differential ability of the lodicules to swell. Here, mutagenesis of the barley cultivar ‘Misato Golden’ (which carries the cly1.b allele), achieved using sodium azide
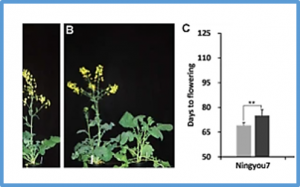
CONSTANS (CO) is a key gene that responds to photoperiod and in Arabidopsis can promote flowering under long-day (LD) conditions. Brassica napus L. is a major oil crop and close relative of Arabidopsis, and arose via allopolyploidization from the diploids B. rapa (A genome) and B. oleracea (C genome). In this study, we confirmed that B. napus has two CO genes located on the A10 (BnaCO.A10) and C9 (BnaCO.C9) chromosomes.
Carrot taproot color results from the accumulation of various carotenoid and anthocyanin pigments. Recently, the Or gene was identified as a candidate gene associated with the accumulation of β-carotene and other provitamin A carotenoids in roots. The specific molecular mechanisms involved with this process, as well as the interactions between Or and the other genes involved in this process are not well understood.
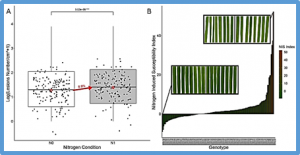
Nitrogen fertilization is known to increase disease susceptibility, a phenomenon called Nitrogen-Induced Susceptibility (NIS). In rice, this phenomenon has been observed in infections with the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. A previous classical genetic study revealed a locus (NIS1) that enhances susceptibility to rice blast under high nitrogen fertilization.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :