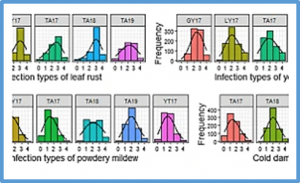
Wheat is a major staple food crop and provides more than one-fifth of the daily calories and dietary proteins for humans. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) and genomic selection (GS) for wheat stress resistance and tolerance related traits are critical to understanding their genetic architecture for improvement of breeding selection efficiency. However, the insufficient marker density in previous studies limited the utility of GWAS and GS in wheat genomic breeding. Here, we conducted a high-resolution GWAS for wheat leaf rust (LR), yellow rust (YR), powdery mildew (PM), and cold tolerance (CT) by genotyping a panel of 768 wheat cultivars using genotyping-by-sequencing.
The potato tuber starch trait is changed depending on the composition of amylose and amylopectin. The amount of amylopectin is determined by the activity of the starch branching enzymes SBE1, SBE2, and SBE3 in potato. SBE3, a homolog of rice BEI, is a major gene that is abundant in tubers. In this study, we created mutants of the potato SBE3 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 attached to the translation enhancer dMac3. Potato has a tetraploid genome, and a four-allele mutant of the SBE3 gene is desired. Mutations in the SBE3 gene were found in 89 of 126 transformants of potato plants.
In autumn 2020, leaf blight was observed on rice (Oryza sativa L., variety Zhongzao39, Yongyou9, Yongyou12, Yongyou15, Yongyou18, Yongyou1540, Zhongzheyou8, Jiafengyou2, Xiangliangyou900 and Jiyou351) in the fields of 17 towns in Zhejiang and Jiangxi Provinces, China. The disease incidence was 45%-60%. Initially, water-soaked, linear, light brown lesions emerged in the upper blades of the leaves, and then spread down to leaf margins, which ultimately caused leaf curling and blight during the booting-harvest stage (Fig. S1)
The concept of genetically modified foods is becoming increasingly popular. Consumer attitude towards GMOs is influenced by various factors, including food safety, quality, and taste. This shows the dire need to understand current consumer attitudes towards GMO (genetically modified organism) products, especially since there are growing concerns locally and globally related to their health, finance, and environmental safety. Hence, the study's objective is to determine the extent to which government information influences and changes current consumer attitude of GMOs. Once consumers were “forced” to read a trusted scientific statement on the safety of GMOs, their concerns about whether is bad for your health or caused cancer decreased significantly.
The narrow genetics of most crops is a fundamental vulnerability to food security. This makes wild crop relatives a strategic resource of genetic diversity that can be used for crop improvement and adaptation to new agricultural challenges. Here, we uncover the contribution of one wild species accession, Arachis cardenasii GKP 10017, to the peanut crop (Arachis hypogaea) that was initiated by complex hybridizations in the 1960s and propagated by international seed exchange. However, until this study, the global scale of the dispersal of genetic contributions from this wild accession had been obscured by the multiple germplasm transfers, breeding cycles, and unrecorded genetic mixing between lineages that had occurred over the years.
Yangmai 158 (Y158) is an elite wheat cultivar widely grown in China with stable Fusarium head blight (FHB) resistance. To enrich the genetic basis underlying FHB resistance, QTL mapping was conducted using two recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations derived from crosses of Y158 with susceptible lines Annong 8455 and Veery. Survey with makers linked to Fhb1, Fhb2, Fhb4 and Fhb5 in resistance cultivar Wangshuibai indicated that both Y158 and the susceptible lines do not contain these QTL.
The aerial surfaces of land plants are coated with a cuticle, comprised of cutin and wax, which is a hydrophobic barrier for preventing uncontrolled water loss and environmental damage. However, the mechanisms by which cuticle components are formed are still unknown in Brassica napus L. and were therefore assessed here. BnA1.CER4 and BnC1.CER4, encoding fatty acyl-coenzyme A reductases localizing to the endoplasmic reticulum and highly expressed in leaves, were identified and functionally characterized.
Aphanomyces root rot (ARR), caused by Aphanomyces euteiches Drechs., is a destructive soilborne disease of field pea (Pisum Sativum L.). No completely resistant pea germplasm is available, and current ARR management strategies rely on partial resistance and fungicidal seed treatments. In this study, an F8 recombinant inbred line population of 135 individuals from the cross ‘Reward’ (susceptible) × ‘00-2067’ (tolerant) was evaluated for reaction to ARR under greenhouse conditions with the A. euteiches isolate Ae-MDCR1
Production of the high-value carotenoid astaxanthin, which is widely used in food and feed due to its strong antioxidant activity and colour, is less efficient in cereals than in model plants. Here, we report a new strategy for expressing β-carotene ketolase and hydroxylase genes from algae, yeasts and flowering plants in the whole seed using a seed-specific bidirectional promoter. Engineered maize events were backcrossed to inbred maize lines with yellow endosperm to generate progenies that accumulate astaxanthin
High temperatures causing heat stress disturb cellular homeostasis and impede growth and development in plants. Extensive agricultural losses are attributed to heat stress, often in combination with other stresses. Plants have evolved a variety of responses to heat stress to minimize damage and to protect themselves from further stress. A narrow temperature window separates growth from heat stress, and the range of temperatures conferring optimal growth often overlap with those producing heat stress.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :