Soil salinity is one of the most significant abiotic stresses hampering plant growth and development, which ultimately translates to reduced crop yield. Soil salinization is exacerbated by excessive use of chemical fertilizers and soil amendments, improper drainage, and seawater ingress. It is estimated that over 6% of the world’s total land area is salt affected, of which over 12 million hectares are irrigated lands posing a serious threat to irrigated agriculture .
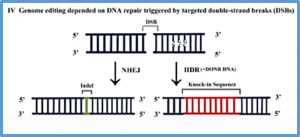
Nurhayati, Ardie SW, Santoso TJ,Sudarsono. 2021. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in rice cv. IPB3Sresults in a semi-dwarf phenotypic mutant.Biodiversitas 22:3792-3800.IPB3Sis Indonesian lowland rice and high-yielding cultivar. However, plant height posture makes itprone tolodging whichcould reduce the yield. This study aimed to edit the GA20Ox2gene by introducing CRISPR/Cas9 GA20Ox2construct into IPB3Sand developing the semidwarf rice mutants.
Zinc (Zn) is an essential mineral element in many organisms. Zn deficiency in humans causes various health problems; therefore, an adequate dietary Zn intake is required daily. Rice, Oryza sativa, is one of the main crops cultivated in Asian countries, and one of the breeding scopes of rice is to increase the grain Zn levels. Previously, we found that an Australian wild rice strain, O. meridionalis W1627, exhibits higher grain Zn levels than cultivated rice, O. sativa Nipponbare, and identified responsible genomic loci.
Salt stress is an important abiotic factor that causes severe losses in soybean yield and quality. Therefore, breeding salt-tolerant soybean germplasm resources via genetic engineering has gained importance. Aspergillus glaucus, a halophilic fungus that exhibits significant tolerance to salt, carries the gene AgGlpF. In this study, we used the soybean cotyledonary node transformation method to transfer the AgGlpF gene into the genome of the soybean variety Williams 82 to generate salt-tolerant transgenic soybean varieties.
Biofortification is one of the strategies developed to address malnutrition in developing countries, the aim of which is to improve the nutritional content of crops. The common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), a staple food in several African and Latin American countries, has excellent nutritional attributes and is considered a strong candidate for biofortification. The objective of this study was to identify genomic regions associated with nutritional content in common bean grains using 178 Mesoamerican accessions belonging to a Brazilian Diversity Panel (BDP) and 25,011 good-quality single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Genome editing, a revolutionary technology in molecular biology and represented by the CRISPR/Cas9 system, has become widely used in plants for characterizing gene function and crop improvement. Tomato, serving as an excellent model plant for fruit biology research and making a substantial nutritional contribution to the human diet, is one of the most important applied plants for genome editing. Using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis, the re-evaluation of tomato genes essential for fruit ripening highlights that several aspects of fruit ripening should be reconsidered.
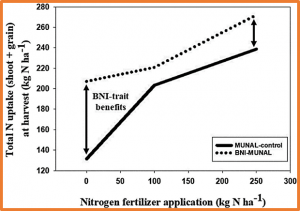
Active nitrifiers and rapid nitrification are major contributing factors to nitrogen losses in global wheat production. Suppressing nitrifier activity is an effective strategy to limit N losses from agriculture. Production and release of nitrification inhibitors from plant roots is termed “biological nitrification inhibition” (BNI). Here, we report the discovery of a chromosome region that controls BNI production in “wheat grass” Leymus racemosus (Lam.) Tzvelev, located on the short arm of the “Lr#3Nsb” (Lr#n),
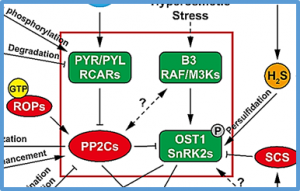
The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) plays a central role in the regulation of stomatal movements under water-deficit conditions. The identification of ABA receptors and the ABA signaling core consisting of PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors, PP2C protein phosphatases and SnRK2 protein kinases has led to studies that have greatly advanced our knowledge of the molecular mechanisms mediating ABA-induced stomatal closure in the past decade. This review focuses on recent progress in illuminating the regulatory mechanisms of ABA signal transduction,
Resistance to stripe rust, a foliar disease caused by the fungus P. striiformis f. sp. tritici, in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is both qualitatively and quantitatively controlled. Resistance genes confer complete, race-specific resistance but are easily overcome by evolving pathogen populations, while quantitative resistance is controlled by many small- to medium-effect loci that provide incomplete yet more durable protection.
We compared the predictive ability of various prediction models for a maize dataset derived from 910 doubled haploid lines from two European landraces (Kemater Landmais Gelb and Petkuser Ferdinand Rot), which were tested at six locations in Germany and Spain. The compared models were Genomic Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (GBLUP) as an additive model, Epistatic Random Regression BLUP (ERRBLUP) accounting for all pairwise SNP interactions,


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :