The foxglove aphid (FA: Aulacorthum solani Kaltenbach) is an important insect pest that causes serious yield losses in soybean. The FA resistance gene Raso2 from wild soybean PI 366121 was previously mapped to a 13 cM interval on soybean chromosome 7. However, fine-mapping of Raso2 was needed to improve the effectiveness of marker-assisted selection (MAS) and to eventually clone it. The objectives of this study were to fine-map Raso2 from PI 366121 using Axiom® 180 K SoyaSNP array, to confirm the resistance and inheritance of Raso2 in a different background, and to identify candidate gene(s).
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-associated protein (Cas) genome editing system (CRISPR-Cas) is revolutionizing agriculture. In this system, a guide sequence that matches to a particular genomic DNA is placed in front of a synthetic RNA that consists of a scaffold sequence necessary for Cas-binding to form a guide RNA (gRNA). gRNA/Cas complex binds to the target DNA that contains a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) via base-paring and generates a double-strand break (DSB) by Cas protein.
Maize is an important crop that is cultivated worldwide. As maize spread across the world, selection for local environments resulted in variation, but the impact on differences between the genome has not been quantified. By producing high-quality genomic sequences of the 26 lines used in the maize nested association mapping panel, Hufford et al. map important traits and demonstrate the diversity of maize. Examining RNA and methylation of genes across accessions, the authors identified a core set of maize genes.
The CRISPR/Cas9 system is now commonly employed for genome editing in various plants such as Arabidopsis, rice, and tobacco. In general, in genome editing of the Arabidopsis genome, the SpCas9 and guide RNA genes are introduced into the genome by the floral dip method. Mutations induced in the target sequence by SpCas9 are confirmed after selecting transformants by screening the T1 seed population. The advantage of this method is that genome-edited plants can be isolated easily.
Rice is a key food security crop in Africa. The importance of rice has led to increasing country-specific, regional and multinational efforts to develop germplasm and policy initiatives to boost production for a more food secure continent. Currently, this critically important cereal crop is predominantly cultivated by small-scale farmers under sub-optimal conditions in most parts of sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). Rice blast disease, caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, represents one of the major biotic constraints to rice production under small-scale farming systems of Africa, and developing durable disease resistance is therefore of critical importance.
Theory identifies factors that can undermine the evolutionary stability of mutualisms. However, theory’s relevance to mutualism stability in nature is controversial. Detailed comparative studies of parasitic species that are embedded within otherwise mutualistic taxa (e.g., fig pollinator wasps) can identify factors that potentially promote or undermine mutualism stability. We describe results from behavioral, morphological, phylogenetic, and experimental studies of two functionally distinct, but closely related, Eupristina wasp species associated with the monoecious host fig, Ficus microcarpa, in Yunnan Province, China.
The cytoplasmic male sterility/fertility restoration (CMS/Rf) system has been extensively used for heterosis in plants. It also provides valuable resources for studying mitochondrial–nuclear coevolution and interaction. The oxa CMS, which is a new CMS type reported in Brassica juncea (B. juncea), has been broadly used in the exploitation and application of heterosis in this species. However, the oxa CMS fertility restorer gene BjRf has not been reported. In this study, a stable restorer line was successfully constructed via continuous testcross and artificial selection.
Phosphorus (P) is an essential element for the growth and development of plants. Soybean (Glycine max) is an important food crop that is grown worldwide. Soybean yield is significantly affected by P deficiency in the soil. To investigate the molecular factors that determine the response and tolerance at low-P in soybean, we conducted a comparative proteomics study of a genotype with low-P tolerance (Liaodou 13, L13) and a genotype with low-P sensitivity (Tiefeng 3, T3) in a paper culture experiment with three P treatments, i.e. P-free (0 mmol·L-1), low-P (0.05 mmol·L-1) and normal-P (0.5 mmol·L-1). A total of 4126 proteins were identified in roots of the two genotypes.
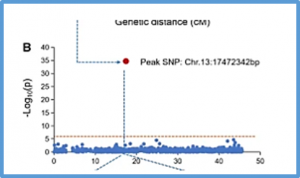
Sclerotinia stem rot (SSR), caused by the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, is one of the most devastating diseases in soybean (Glycine max (Linn.) Merr.) However, the genetic architecture underlying soybean resistance to SSR is poorly understood, despite several mapping and gene mining studies. In the present study, the identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) involved in the resistance to S. sclerotiorum was conducted in two segregating populations
The gymnosperm Welwitschia mirabilis belongs to the ancient, enigmatic gnetophyte lineage. It is a unique desert plant with extreme longevity and two ever-elongating leaves. We present a chromosome-level assembly of its genome (6.8 Gb/1 C) together with methylome and transcriptome data to explore its astonishing biology. We also present a refined, high-quality assembly of Gnetum montanum to enhance our understanding of gnetophyte genome evolution.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :