The study shows that seed dressing with TFM resulted in elevated levels of oxalic acid, flavonoids, phenolic substances, callose and other compounds associated with Nilaparvata lugens resistance in rice plants, and low TFM residue content in rice plant stem and grain. Host choice behavioral experiments showed that N. lugens females prefer feeding on untreated rice plants.
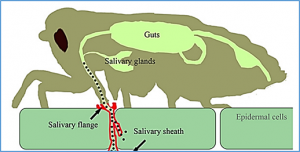
The importin α family belongs to the conserved nuclear transport pathway in eukaryotes. However, the biological functions of importin α in the plasma membrane are still elusive. Here, we report that importin α, as a plasma membrane–associated protein, is exploited by the rice stripe virus (RSV) to enter vector insect cells, especially salivary gland cells. When the expression of three importin α genes was simultaneously knocked down, few virions entered the salivary glands of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus. Through hemocoel inoculation of virions, only importin α2 was found to efficiently regulate viral entry into insect salivary-gland cells. Importin α2 bound the nucleocapsid protein of RSV with a relatively high affinity through its importin β–binding (IBB) domain, with a dissociation constant KD of 9.1 μM.
Manihot esculenta (cassava) is a root crop originating from South America that is a major staple in the tropics, including in marginal environments. This study focused on South American and African germplasm and investigated the genetic architecture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN), a major component of root quality. HCN, representing total cyanogenic glucosides, is a plant defense component against herbivory but is also toxic for human consumption. We genotyped 3354 landraces and modern breeding lines originating from 26 Brazilian states and 1389 individuals were phenotypically characterized across multi-year trials for HCN. All plant material was subjected to high-density genotyping using genotyping by sequencing.
Phenotypic information of crop genetic resources is a prerequisite for an informed selection that aims to broaden the genetic base of the elite breeding pools. We investigated the potential of genomic prediction based on historical screening data of plant responses against the Barley yellow mosaic viruses for populating the bio-digital resource center of barley.
Xanthomonas oryzae (Xo) is one of the important pathogenic bacterial groups affecting rice production. Its pathovars Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc) cause bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak in rice, respectively. Xo infects host plants by relying mainly on its transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) that bind to host DNA targets, named effector binding elements (EBEs), and induce the expression of downstream major susceptibility genes. Blocking TALE binding to EBE could increase rice resistance to the corresponding Xo.
We investigated resistance to pathotypically variable Phytophthora sojae isolates in the soybean variety Tosan-231, which has broad-spectrum resistance. Mapping analysis using descendent lines from a cross between Shuurei and Tosan-231 demonstrated that a genomic region between SSR markers BARCSOYSSR_03_0209 and BARCSOYSSR_03_0385 (termed “Region T”), confers broad-spectrum resistance in Tosan-231 and contains three closely linked resistance loci.
Heat stress, exacerbated by global warming, has a negative influence on wheat production worldwide and climate resilient cultivars can help mitigate these impacts. Selection decisions should therefore depend on multi-environment experiments representing a range of temperatures at critical stages of development. Here, we applied a meta-genome wide association analysis (metaGWAS) approach to detect stable QTL with significant effects across multiple environments.
Wheat is a staple food crop consumed by more than 30% of world population. Nitrogen (N) fertilizer has been applied broadly in agriculture practice to improve wheat yield to meet the growing demands for food production. However, undue N fertilizer application and the low nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of modern wheat varieties are aggravating environmental pollution and ecological deterioration. In rice, an are1 mutant possesses the increased NUE under nitrogen-limiting conditions, delayed senescence and consequently increased grain yield.
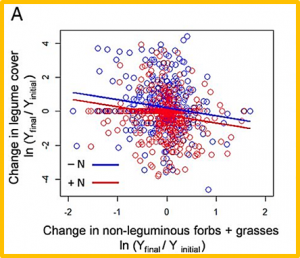
Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment is driving global biodiversity decline and modifying ecosystem functions. Theory suggests that plant functional types that fix atmospheric nitrogen have a competitive advantage in nitrogen-poor soils, but lose this advantage with increasing nitrogen supply. By contrast, the addition of phosphorus, potassium, and other nutrients may benefit such species in low-nutrient environments by enhancing their nitrogen-fixing capacity. We present a global-scale experiment confirming these predictions for nitrogen-fixing legumes (Fabaceae) across 45 grasslands on six continents.
Proteins are essential to life, and understanding their structure can facilitate a mechanistic understanding of their function. Through an enormous experimental efort1–4 , the structures of around 100,000 unique proteins have been determined5 , but this represents a small fraction of the billions of known protein sequences6,7 . Structural coverage is bottlenecked by the months to years of painstaking efort required to determine a single protein structure. Accurate computational approaches are needed to address this gap and to enable large-scale structural bioinformatics.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :