Anther culture, a doubled haploid (DH) technique, has become an important technology in many plant-breeding programmes. Although anther culturability is the key factor in this technique, its genetic mechanisms in rice remain poorly understood. In this study, we mapped quantitative trait loci (QTLs) responsible for anther culturability by using 192 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from YZX (Oryza sativa ssp. indica) × 02428 (Oryza sativa ssp. japonica) and a high-density bin map. A total of eight QTLs for anther culturability were detected in three environments.
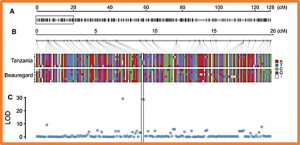
The root-knot nematode [Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid & White) Chitwood] (RKN) causes significant storage root quality reduction and yields losses in cultivated sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.]. In this study, resistance to RKN was examined in a mapping population consisting of 244 progenies derived from a cross (TB) between ‘Tanzania,’ a predominant African landrace cultivar with resistance to RKN, and ‘Beauregard,’ an RKN susceptible major cultivar in the USA. We performed quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis using a random-effect QTL mapping model on the TB genetic map.
Rice blast and bacterial blight are important diseases of rice (Oryza sativa) caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae and the bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), respectively. Breeding rice varieties for broad-spectrum resistance is considered the most effective and sustainable approach to controlling both diseases. Although dominant resistance genes have been extensively used in rice breeding and production,
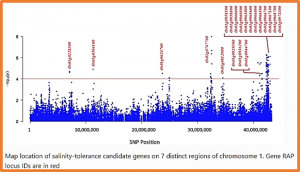
Under stress conditions 151 trait-marker associations were identified that were scattered on 10 chromosomes of rice that arranged in 29 genomic regions. A genomic region on chromosome 1 (11.26 Mbp) was identified which co-located with a known QTL region SalTol1 for salinity tolerance at vegetative stage. A candidate gene (Os01g0304100) was identified in this region which encodes a cation chloride cotransporter.
We propose a novel computational method, SequencErr, to address this challenge by measuring the base correspondence between overlapping regions in forward and reverse reads. An analysis of 3777 public datasets from 75 research institutions in 18 countries revealed the sequencer error rate to be ~ 10 per million (pm) and 1.4% of sequencers and 2.7% of flow cells have error rates > 100 pm.
Climate change and an additional 3 billion mouths to feed by 2050 raise serious concerns over global food security. Crop breeding and land management strategies will need to evolve to maximize the utilization of finite resources in coming years. High-throughput phenotyping and genomics technologies are providing researchers with the information required to guide and inform the breeding of climate smart crops adapted to the environment.
In enhancing the resilience of our crops to the impacts of climate change, selection objectives need to address increased variability in the production environment. This encompasses the effects of more variable rainfall and temperatures than currently experienced, including extreme weather events, and changes in pest and pathogens distribution with the increased likelihood of major pest and disease outbreaks as well as occurrence of novel pathogens.
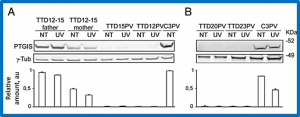
The cancer-free photosensitive trichothiodystrophy (PS-TTD) and the cancer-prone xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) are rare monogenic disorders that can arise from mutations in the same genes, namely ERCC2/XPD or ERCC3/XPB. Both XPD and XPB proteins belong to the 10-subunit complex transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) that plays a key role in transcription and nucleotide excision repair, the DNA repair pathway devoted to the removal of ultraviolet-induced DNA lesions.
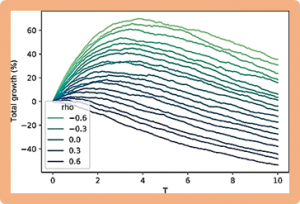
We develop a mathematical theory of how natural selection operates in the presence of interaction between replicating units. Our results show that with interaction, natural selection does more than seek to selfishly maximize fecundity. It also seeks to minimize correlation of fecundity between replicating units. We argue that correlation is a mechanism by which evolution can select for cooperation.
In the coming decades, larger genetic gains in yield will be necessary to meet projected demand, and this must be achieved despite the destabilizing impacts of climate change on crop production. The root systems of crops capture the water and nutrients needed to support crop growth, and improved root systems tailored to the challenges of specific agricultural environments could improve climate resiliency.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :