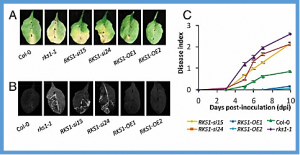
The site-specific nuclease-based CRISPR/Cas9 system has emerged as one of the most efficient genome editing tools to modify multiple genomic targets simultaneously in various organisms, including plants for both fundamental and applied researches. Screening for both on-target and off-target mutations in CRISPR/Cas9-generated mutants at the early stages is an indispensable step for functional analysis and subsequent application.
Quantitative disease resistance (QDR) represents the predominant form of resistance in natural populations and crops. Surprisingly, very limited information exists on the biomolecular network of the signaling machineries underlying this form of plant immunity. This lack of information may result from its complex and quantitative nature. Here, we used an integrative approach including genomics, network reconstruction,
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is generally sensitive to low temperatures, and in production systems that use direct-seeding, low-temperature germinability (LTG) is a desired trait. Previously, the QTLs, qLTG1 and qLTG3, that control LTG, were mapped using the BC4F8 population, which is a cross of Korean elite cultivar Hwaseong and O. rufipogon (IRGC 105491). We have characterized and analyzed the interaction between the two QTLs, by crossing TR20 that has O. rufipogon alleles at qLTG1 and qLTG3 in a Hwaseong background, with Hwaseong, to develop an F2 population.
In this study, we compared genome-wide transcriptome profile of two rice hybrids, one with (test hybrid IR79156A/IL50-13) and the other without (control hybrid IR79156A/KMR3) O. rufipogon introgressions to identify candidate genes related to grain yield in the test hybrid. IL50-13 (Chinsurah Nona2 IET21943) the male parent (restorer) used in the test hybrid, is an elite BC4F8 introgression line of KMR3 with O. rufipogon introgressions. We identified 2798 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in flag leaf and 3706 DEGs in panicle. Overall, 78 DEGs were within the major yield QTL qyld2.1 and 25 within minor QTL qyld8.2.
The exploitation of novel alleles from wild rice that were lost during rice cultivation could be very important for rice breeding and evolutionary studies. Plant height (PH) was a target of artificial selection during rice domestication and is still a target of modern breeding. The "green revolution" gene semi-dwarf 1 (SD1) were well documented and used in the past decades, allele from wild rice could provide new insights into the functions and evolution of this gene.
Oryza rufipogon and O. longistaminata are important wild relatives of cultivated rice, harboring a promising source of novel genes for rice breeding programs. Here, we present de novo assembled draft genomes and annotation of O. rufipogon and O. longistaminata. Our analysis reveals a considerable number of lineage-specific gene families associated with the self-incompatibility (SI) and formation of reproductive separation.
Asian cultivated rice is believed to have been domesticated from a wild progenitor, Oryza rufipogon, offering promising sources of alleles for world rice improvement. Here we first present a high-quality chromosome-scale genome of the typical O. rufipogon. Comparative genomic analyses of O. sativa and its two wild progenitors, O. nivara and O. rufipogon, identified many dispensable genes functionally enriched in the reproductive process.
A total of 94 blast isolates were collected from five provinces in the Mekong River Delta in southern Vietnam. The pathogenicities of these isolates were evaluated using 25 international differential varieties (DVs) covering 23 resistance genes and a susceptible Chinese cultivar, Lijiangxintuanheigu (LTH). Based on the reaction patterns of the DVs, the isolates were classified into two clusters (I and II).
Awns are bristle-like organs at the tips of the glumes. Wild rice has maintained long awns for successful seed propagation through seed dispersal. Seed awning is an interesting trait in rice domestication. Long awns might have been beneficial for seed gatherers in the initial phase of domestication; however, awnless phenotypes were preferably selected in a later phase with non-seed-shattering plants. Investigation of domestication loci associated with awnlessness in cultivated rice will be useful in clarifying the process and history of rice domestication.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are about 22 nucleotides regulatory non-coding RNAs that play versatile roles in reprogramming plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. However, it remains unknown whether miRNAs confer the resistance to necrotrophic fungus Rhizoctonia solani in rice. To investigate whether miRNAs regulate the resistance to R. solani, we constructed 12 small RNA libraries from susceptible and resistant rice cultivars treated with water/pathogen at 5 h post inoculation (hpi), 10 hpi and 20 hpi, respectively.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :