The present study evaluated submergence responses in 88 lowland indigenous rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces from Koraput, India, to identify submergence-tolerant rice genotypes. In pot experiments, variations in survival rate, shoot elongation, relative growth index, dry matter, chlorophyll, soluble sugar and starch contents were evaluated in two consecutive years under well-drained and completely submerged conditions.
Grain size is one of the critical agronomic traits governing grain yield and quality in rice. However, the underlying genetic mechanisms that control grain size in rice are poorly understood. We used an introgression line derived from Zhonghui 8015 and Oryza rufipogon Griff.
Rice varieties having high Fe concentration in the endospermic region can be used as a good source for Fe deficit population. In this study, 303 Oryza sativa varieties and 1 Oryza rufipogon accession were assessed for spatial Fe accumulation in grains by Prussian blue staining method. Spatial ferritin protein distribution in grains was visualized by immunohistochemistry, and ferritin expression was assessed in selected rice varieties using semi-quantitative reverse transcription PCR.
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the genetic diversity and the pathogenicity of some Vietnamese rice blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae Barr) populations collected from four specific different areas in Central Vietnam by using molecular analysis. The results showed that the virulence range-isolate of the blast population is highly varied. By using the polymorphic RAPD markers for genetic diversity evaluation of 32 M. oryzae isolates,
Rice is a major staple food that sustains more than three billion people in the world. However, as the world’s population continues to grow, it has become more and more urgent to develop super high yielding varieties as well as hyper-tolerant varieties to pathogens and climate change. Genome editing technology is gradually revolutionizing crop improvement by facilitating a rapid, efficient and simple strategy for modification of target genes. Since many genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) involved in agronomically important traits have already been determined by comparative genomics, GWAS and OMICS-based approaches, genome editing could provide the ultimate tool to accelerate the breeding of new mutations that has until now been conducted by random mutagenesis.
The cassava genome possesses 14 of the 17 plant PR families, with a total of 447 PR genes. A cassava PR gene nomenclature is proposed. Phylogenetic relatedness of cassava PR proteins to each other and to homologs in poplar, rice and Arabidopsis identified cassava-specific PR gene family expansions. The temporal programs of PR gene expression in response to the whitefly (Aleurotrachelus socialis) in four whitefly-susceptible cassava genotypes showed that 167 of the 447 PR genes were regulated after whitefly infestation.
Cassava is highly tolerant to stressful conditions, especially drought stress conditions; however, the mechanisms underlying this tolerance are poorly understood. The GRAS gene family is a large family of transcription factors that are involved in regulating the growth, development, and stress responses of plants. Currently, GRAS transcription factors have not been systematically studied in cassava, which is the sixth most important crop in the world.
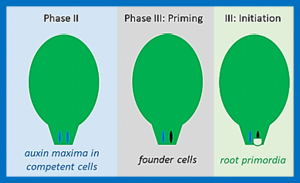
Many plant species are able to regenerate adventitious roots either directly from aerial organs such as leaves or stems, in particularly after detachment (cutting), or indirectly, from over-proliferating tissue termed callus. In agriculture, this capacity of de novo root formation from cuttings can be used to clonally propagate several important crop plants including cassava, potato, sugar cane, banana and various fruit or timber trees
Aflatoxin contamination in peanuts caused by Aspergillus flavus is a serious food safety issue for human health around the world. Host plant resistance to fungal infection and reduction in aflatoxin are crucial for mitigating this problem. Identification of the resistance-linked markers can be used in marker-assisted breeding for varietal development. Here we report construction of two high-density genetic linkage maps with 1975 SNP loci and 5022 SNP loci, respectively.
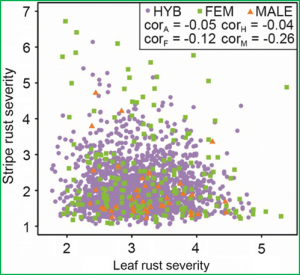
Leaf rust and stripe rust belong to the most important fungal diseases in wheat production. Due to a dynamic development of new virulent races, epidemics appear in high frequency and causes significant losses in grain yield and quality. Therefore, research is needed to develop strategies to breed wheat varieties carrying highly efficient resistances. Stacking of dominant resistance genes through hybrid breeding is such an approach. Within this study, we investigated the genetic architecture of leaf rust and stripe rust resistance of 1750 wheat hybrids and their 230


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :