Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) is a major crop extensively cultivated in the tropics as both an important source of calories and a promising source for biofuel production. Although stable gene expression have been used for transgenic breeding and gene function study, a quick, easy and large-scale transformation platform has been in urgent need for gene functional characterization, especially after the cassava full genome was sequenced.
There is a wide range of end-use products made from cereal grains, and these products often demand different grain characteristics. Fortunately, cereal crop species including sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] contain high phenotypic variation for traits influencing grain quality. Identifying genetic variants underlying this phenotypic variation allows plant breeders to develop genotypes with grain attributes optimized for their intended usage.
Low temperature may exert a negative impact on agronomical productivity. PsbR was known as the 10 kDa Photosystem II polypeptide. Although plant PsbR is thought to play important roles in photosynthesis, little is known about the contribution of plant PsbR to abiotic stress resistance. The expression patterns of three OsPsbR gene family members, OsPsbR1, OsPsbR2, and OsPsbR3, were characterized in rice ‘Nipponbare’.
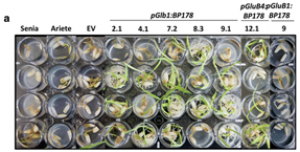
A synthetic gene encoding the BP178 peptide was prepared and introduced in rice plants. The gene was efficiently expressed in transgenic rice under the control of an endosperm-specific promoter. Among the three endosperm-specific rice promoters (Glutelin B1, Glutelin B4 or Globulin 1), best results were obtained when using the Globulin 1 promoter. The BP178 peptide accumulated in the seed endosperm and was easily recovered from rice seeds using a simple procedure with a yield of 21 μg/g. The transgene was stably inherited for at least three generations, and peptide accumulation remained stable during long term storage of transgenic seeds.
Plant leaves form at the flanks of the shoot apical meristem in response to cues provided by the phytohormone auxin. Auxin signals determine the sites of leaf initiation and bulging, a process followed by gradual and ongoing differentiation of leaf tissues. We show here that the tomato ethylene response factor-type transcription factor LEAFLESS is induced by, and necessary for, auxin-triggered leaf initiation.
Genetic imprinting refers to the unequal expression of paternal and maternal alleles of a gene in sexually reproducing organisms, including mammals and flowering plants. Although many imprinted genes have been identified in plants, the functions of these imprinted genes have remained largely uninvestigated. We report genome-wide analysis of gene expression
Epidemiological evidence suggests that vitamin D can protect women from developing breast cancer (BC). This study reveals that vitamin D and its receptor regulate autophagy in both normal mammary epithelial cells and luminal BCs, and suggests a potential mechanism underlying the link between vitamin D levels and BC risk. In addition, this work suggests that vitamin D receptor ligands could be exploited therapeutically for the treatment of a significant subset of BCs.
Epigenetic mechanisms are crucial mediators of appropriate plant reactions to adverse environments, but their involvement in long-term adaptation is less clear. Here, we established two rice epimutation accumulation lines by applying drought conditions to 11 successive generations of two rice varieties. We took advantage of recent technical advances to examine the role of DNA methylation variations on rice adaptation to drought stress. We found that multi-generational drought improved the drought adaptability of offspring in upland fields.
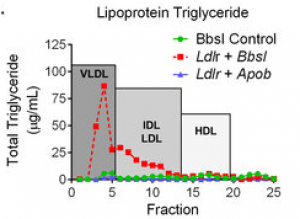
Germline manipulation using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing has dramatically accelerated the generation of new mouse models. Nonetheless, many metabolic disease models still depend upon laborious germline targeting, and are further complicated by the need to avoid developmental phenotypes.
Four genetically modified (GM) maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids (coleopteran resistant, coleopteran and lepidopteran resistant, lepidopteran resistant and herbicide tolerant, coleopteran and herbicide tolerant) and its non-GM control maize stands were tested to compare the functional diversity of arthropods and to determine whether genetic modifications alter the structure of arthropods food webs. A total number of 399,239 arthropod individuals were used for analyses.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :