Avirulence genes in Magnaporthe oryzae, the fungal pathogen that causes the devastating rice blast disease, have been documented to be major targets subject to mutations to avoid recognition by resistance (R) genes. In this study, an avirulence (AVR) gene-based diagnosis tool for determining the virulence spectrum of a rice blast pathogen population was developed and validated. A set of 77 single-spore field isolates was subjected to pathotype analysis using differential lines each containing a single R gene and classified into 20 virulent pathotypes except for four isolates that lost pathogenicity.
The dwarf or compact plant architecture is an important trait in plant breeding. A number of genes controlling plant height have been cloned and functionally characterized which often involve in biosynthesis or signaling of plant hormones such as brassinosteroids (BRs). No genes for plant height or vine length have been cloned in cucurbit crops (family Cucurbitaceae).
Hybrid seed lethality has been recognized and addressed by a long-standing tradition of plant-breeding research. Nevertheless, its role in evolution and speciation has been underestimated. In this study, hybrid seed lethality between Arabidopsis lyrata and Arabidopsis arenosa, two model species of growing interest in the scientific community, was investigated.
The plant ferredoxin-like protein (PFLP) gene, cloned from sweet peppers predicted as an electron carrier in photosynthesis, shows high homology to the Fd-I sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana, Lycopersicon esculentum, Oryza sativa and Spinacia oleracea. Most of pflp related studies focused on anti-pathogenic effects, while less understanding for the effects in photosynthesis with physiological aspects, such as photosynthesis rate, and levels of carbohydrate metabolites.
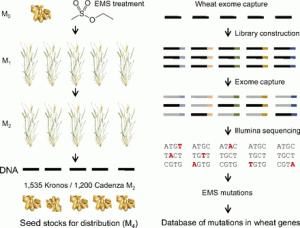
Pasta and bread wheat are polyploid species that carry multiple copies of each gene. Therefore, loss-of-function mutations in one gene copy are frequently masked by functional copies on other genomes. We sequenced the protein coding regions of 2,735 mutant lines and developed a public database including more than 10 million mutations. Researchers and breeders can search this database online, identify mutations in the different copies of their target gene, and request seeds to study gene function or improve wheat varieties
Maize chlorotic dwarf virus (MCDV), a member of the genus Waikavirus, family Secoviridae, has a 11784 nt (+)ssRNA genome that encodes a 389kDa proteolytically processed polyprotein. We show that the N-terminal 78kDa polyprotein (R78) of MCDV acts as a suppressor of RNA silencing in a well-established assay system. We further demonstrate that R78 is cleaved by the viral 3C-like protease into 51 and 27kDa proteins (p51 and p27), and that p51 is responsible for silencing suppressor activity.
Food legumes play an important role in attaining both food and nutritional security along with sustainable agricultural production for the well-being of humans globally. The various traits of economic importance in legume crops are complex and quantitative in nature, which are governed by quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Mapping of quantitative traits is a tedious and costly process, however, a large number of QTLs has been mapped in soybean for various traits albeit their utilization in breeding programmes is poorly reported.
Mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) is one of the most important leguminous food crops in Asia. We employed Illumina paired-end sequencing to analyse transcriptomes of three different mungbean genotypes. A total of 38.3-39.8 million pairedend reads with 73 bp lengths were generated. The pooled reads from the three libraries were assembled into 56,471 transcripts. Following a cluster analysis,
DNA methylation on cytosine residues is known to affect gene expression and is potentially responsible for the phenotypic variations among different crop cultivars. Here, we present the whole-genome DNA methylation profiles and assess the potential effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for two mungbean cultivars, Sunhwanogdu (VC1973A) and Kyunggijaerae#5 (V2984).
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers are the method of choice for genetic analyses including diversity and quantitative trait loci (QTL) studies. Marker validation is essential for QTL studies, but the cost and workload are considerable when large numbers of markers need to be verified. Marker systems with low development costs would be most suitable for this task.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :