Controlling gene expression in mammalian brain is of utmost importance to causally link the role of gene function to cell circuit dynamics under normal conditions and disease states. We have developed recombinant adeno-associated viruses equipped with tetracycline-controlled genetic switches for inducible and reversible control of gene expression in a cell type specific and brain subregion selective manner.
Using a newly developed technology, HaloTag nucleic acid programmable protein array (HaloTag-NAPPA), we increase the capacity of in situ protein microarray technology several-fold, such that proteome-scale screening becomes feasible. Many examples of novel protein–protein interactions (PPIs) among plant signaling pathways were observed. With few exceptions, nearly all of these connections are undocumented in the existing literature.
Gene copy number variation plays an important role in genome evolution and the penetrance of phenotype variations within a species. We have applied new sequencing and physical mapping strategies to obtain long chromosomal regions from a single DNA preparation in each method that comprise tandem repeated gene copies interspersed with transposable elements that comprise about 85% of the genome. This approach should reduce the time and cost to study haplotype variation of complex genomes like those from mammalian and plant species.
Magnaporthe oryzae is a cereal pathogen causing 20%-30% rice yield losses. Regulatory Factor X transcription factors are highly conserved proteins with diverse functions among organisms. Here, we show that MoRfx1 is required for cell division, development, and pathogenicity in M. oryzae. Deletion of MoRFX1 resulted in reduced growth and conidiation, lowered appressorium turgor, and impaired virulence.
Strong directional selection occurred during the domestication of maize from its wild ancestor teosinte, reducing its genetic diversity, particularly at genes controlling domestication-related traits. Nevertheless, variability for some domestication-related traits is maintained in maize. The genetic basis of this could be sequence variation at the same key genes controlling maize-teosinte differentiation
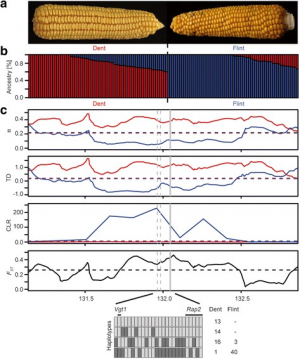
Dent and Flint represent two major germplasm pools exploited in maize breeding. Several traits differentiate the two pools, like cold tolerance, early vigor, and flowering time. A comparative investigation of their genomic architecture relevant for quantitative trait expression has not been reported so far.
Salinity is one of the major limitations to wheat production worldwide. This study was designed to evaluate the level of genetic variation among 150 internationally derived wheat genotypes for salinity tolerance at germination, seedling and adult plant stages, with the aim of identifying new genetic resources with desirable adaptation characteristics for breeding programmes and further genetic studies.
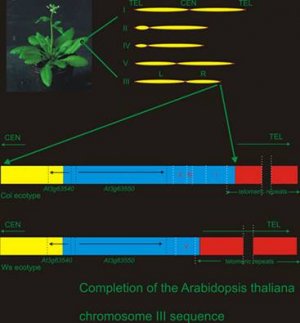
Despite widespread reports on deciphering the sequences of all kinds of genomes, most of these reconstructed genomes rely on a comparison of short DNA sequencing reads to a reference sequence, rather than being independently reconstructed. This method limits the insights on genomic differences to local, mostly small-scale variation, because large rearrangements are likely overlooked by current methods. We have de novo assembled the genome of a common strain of Arabidopsis thaliana Landsberg erecta and revealed hundreds of rearranged regions.
Magnaporthe oryzae is a rice blast fungus and plant pathogen that causes a serious rice disease and, therefore, poses a threat to the world's second most important food security crop. Plant transformation technology has become an adaptable system for cultivar improvement and to functionally analyze genes in plants. The objective of this study was to determine the effects (through over-expressing and using the CaMV 35S promoter) of Pikh on MR219 resistance because it is a rice variety that is susceptible to the blast fungus pathotype P7.2.
In wheat, grain filling is closely related to flag leaf characteristics and function. Stomata are specialized leaf epidermal cells which regulate photosynthetic CO2 uptake and water loss by transpiration. Understanding the mechanisms controlling stomatal size, and their opening under drought, is critical to reduce plant water loss and maintain a high photosynthetic rate which ultimately leads to elevated yield.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :