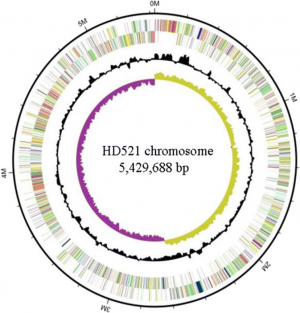
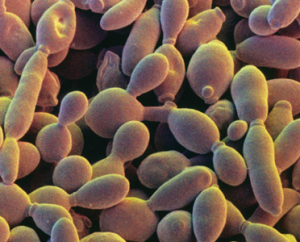
Bacillus thuringiensis is the most widely used biological pesticide in the world. It belongs to the Bacillus cereus sensu lato group, which contains six species. Among these six species, B. thuringiensis, B. anthracis, and B. cereus have a low genetic diversity. B. thuringiensis strain HD521 shows maroon colony which is different from most of the B. thuringiensis strains.
Seed weight is a complex trait controlled by polygenes, and its underlying regulatory mechanisms, especially those involving polyploidy crops, remain elusive. Brassica napus L., which is the second leading crop source of vegetable oil around the world, is an important tetraploid (4×) crop. Our results have generated three significant findings. (i) By combining the linkage and associated analysis,
Bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak are serious, economically damaging, diseases of rice caused by the bacteria Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 was shown to possess biocontrol activity against these Xanthomonas strains by producing the antibiotic compounds difficidin and bacilysin. Analyses using fluorescence, scanning electron and transmission electron microscopy revealed difficidin and bacilysin caused changes in the cell wall and structure of Xanthomonas.
Artemisinin is highly effective against multidrug-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum, the aetiological agent of the most severe form of malaria. However, a low level of accumulation of artemisinin in Artemisia annua is a major limitation for its production and delivery to malaria endemic areas of the world. While several strategies to enhance artemisinin have been extensively explored, enhancing storage capacity in trichome has not yet been considered.
The brown rice plant hopper (BRPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stal), is one of the most important insect pests affecting rice and causes serious damage to the yield and quality of rice plants in Asia. This study used bionic electronic nose technology to sample BRPH volatiles, which vary in age and amount. Principal component analysis (PCA), linear discrimination analysis (LDA), probabilistic neural network (PNN),
We demonstrate that the fission yeast telomerase RNA has a stem terminus element (STE) that it is essential for telomerase action in vivo and in vitro. Using a partial loss-of-function STE allele, we show that the STE is required for wild-type telomeric sequence. This is the first example, to our knowledge, of a sequence that is not part of the telomerase RNA core region that affects the sequence of telomeric DNA.
The spontaneous emergence of stable coexistence between competing lineages in experimental evolution illustrates principles behind the creation and maintenance of biodiversity. Here, we present the first experimental observation of a general mechanism that leads to stable diversification in microbial populations despite competition for shared resources. Coexistence in our system depends on a tradeoff between growth and the ability to avoid cellular crowding.
The rice endophyte Harpophora oryzae shares a common pathogenic ancestor with the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Direct comparison of the interactions between a single plant species and two closely-related (1) pathogenic and (2) mutualistic fungi species can improve our understanding of the evolution of the interactions between plants and fungi that lead to either mutualistic or pathogenic interactions.
Evolution in variable environments depends crucially on the fates of new mutations in the face of fluctuating selection pressures. In constant environments, the relationship between the selective effect of a mutation and the probability that it will eventually fix or go extinct is well understood. However, our understanding of fixation probabilities in fluctuating environmental conditions is limited. Here, we show that temporal fluctuations in environmental conditions can have dramatic effects on the fate of each new mutation, reducing the efficiency of natural selection and increasing the fixation probability of all mutations, including those that are strongly deleterious on average.
Storage lipid is a vital component for maintaining structure of seed storage substances and valuable for rice quality and food texture. However, the knowledge of lipid transporting related genes and their function in seed development have not been well elucidated yet. In this study, we identified OsLTPL36, a homolog of putative lipid transport protein, and showed specific expression in rice developing seed. Transcriptional profiling and in situ hybridization analysis confirmed that OsLTPL36 was exclusively expressed in developing seed coat and endosperm aleurone cells.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :