The brown rice plant hopper (BRPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stal), is one of the most important insect pests affecting rice and causes serious damage to the yield and quality of rice plants in Asia. This study used bionic electronic nose technology to sample BRPH volatiles, which vary in age and amount. Principal component analysis (PCA), linear discrimination analysis (LDA), probabilistic neural network (PNN), BP neural network (BPNN) and loading analysis (Loadings) techniques were used to analyze the sampling data.
Plant protease inhibitors are a structurally highly diverse and ubiquitous class of small proteins, which play various roles in plant development and defense against pests and pathogens. Particular isoforms inhibit in vitro proteases and other enzymes that are not their natural substrates, for example proteases that have roles in human diseases.
Blast caused by fungal Magnaporthe oryzae is a devastating disease of rice worldwide, and this fungus also infects barley. At least 11 rice WRKY transcription factors have been reported to regulate rice response to M. oryzae either positively or negatively. However, the relationships of these WRKYs in the rice defense signaling pathway against M. oryzae are unknown. Previous studies have revealed that rice WRKY13 (as a transcriptional repressor) and WRKY45-2 enhance resistance to M. oryzae.
In a study on the correlation between tryptamine levels and sakuranetin accumulation in the Sekiguchi lesion mutant (SLM) of rice, accumulation was found to be light dependent after inoculation with Magnaporthe oryzae. It was also induced by treatment with tryptamine under white light, but not in the dark. Light-dependent sakuranetin accumulation induced by tryptamine treatment or by infection with M. oryzae was significantly inhibited in the leaves pretreated with metalaxyl, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.
The draft genome of Tibetan hulless barley provides a robust framework to better understand Poaceae evolution and a substantial basis for functional genomics of crop species with a large genome. The expansion of stress-related gene families in Tibetan hulless barley implies that it could be considered as an invaluable gene resource aiding stress tolerance improvement in Triticeae crops.
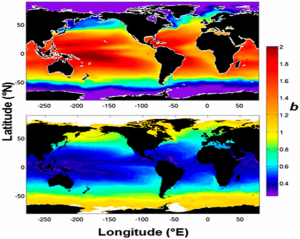
A key factor regulating the air−sea balance of carbon dioxide (CO2) is the sinking of particles containing organic carbon from the surface to the deep ocean. The depth at which this carbon is released back into the water (remineralization) has a strong influence on atmospheric CO2 concentration. Here we show a significant relationship between the remineralization depth of sinking organic carbon flux in the upper ocean and water temperature
NAC proteins are plant-specific transcription factors (TFs). Although they play a pivotal role in regulating distinct biological processes, TFs in maize are yet to be investigated comprehensively. Within the maize genome, we identified 152 putative NAC domain-encoding genes (ZmNACs), including eight membrane-bound members, by systematic sequence analysis and physically mapped them onto ten chromosomes of maize
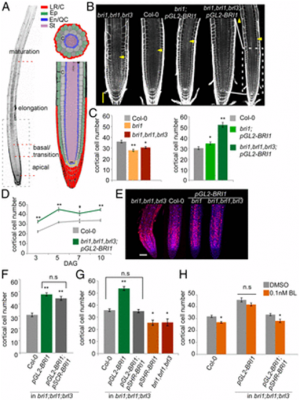
Brassinosteroid (BR) differentially regulates the number of stem cell daughters in the root meristem. How its activity coordinates and maintains the meristem size remains unknown. We show that BR signal coordinates root growth by evoking distinct and often opposing responses in specific tissues. Whereas epidermal BR signal promotes stem cell daughter proliferation, the stele-derived BR signal induces their differentiation
Gene targeting (GT) refers to the designed modification of genomic sequence(s) through homologous recombination (HR). GT is a powerful tool both for the study of gene function and for molecular breeding. However, in transformation of higher plants, non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) occurs overwhelmingly in somatic cells, masking HR-mediated GT. Positive-negative selection (PNS) is an approach for finding HR-mediated GT events because it can eliminate NHEJ effectively by expression of a negative-selection marker gene
The development of superbugs becomes an issue due to its threats to human health. This is due to the increased antibiotic resistance of certain infectious organisms such as bacteria affecting the safety of animal and the quality of its products. With this, Colorado State University researchers, Dr. Paul Morey and Dr. Keith Belk are leading the study of the process and mechanism involved in the development of superbugs in beef and dairy cattle industry.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :