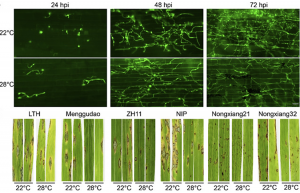
Changes in global temperatures profoundly affect the occurrence of plant diseases. It is well known that rice blast can easily become epidemic in relatively warm weather. However, the molecular mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we show that enhanced blast development at a warm temperature (22°C) compared with the normal growth temperature (28°C) is rice plant-determined. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed that jasmonic acid (JA) biosynthesis and signaling genes in rice could be effectively induced by Magnaporthe oryzae at 28°C but not at 22°C.
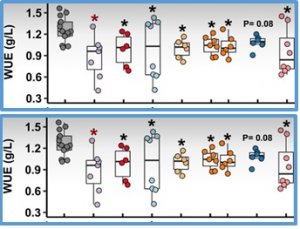
Water-use efficiency (WUE) is the ratio of biomass produced per unit of water consumed; thus, it can be altered by genetic factors that affect either side of the ratio. In the present study, we exploited natural variation for WUE to discover loci affecting either biomass accumulation or water use as factors affecting WUE. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using integrated WUE measured through carbon isotope discrimination (δ13C) of Arabidopsis thaliana accessions identified genomic regions associated with WUE.
The circadian clock is a timekeeping, homeostatic system that temporally coordinates all major cellular processes. The function of the circadian clock is compensated in the face of variable environmental conditions ranging from normal to stress-inducing conditions. Salinity is a critical environmental factor affecting plant growth, and plants have evolved the SALT OVERLY SENSITIVE (SOS) pathway to acquire halotolerance.
In the evolutionary history of plants, variation in cis-regulatory elements (CREs) resulting in diversification of gene expression has played a central role in driving the evolution of lineage-specific traits. However, it is difficult to predict expression behaviors from CRE patterns to properly harness them, mainly because the biological processes are complex. In this study, we used cistrome datasets and explainable convolutional neural network (CNN)
Wheat breeders select heading date to match the most favorable conditions for their target environments and this is favored by the extensive genetic variation for this trait that has the potential to be further explored. In this study, we used a germplasm with broad geographic distribution and tested it in multi-location field trials across Germany over three years. The genotypic response to the variation in the climatic parameters depending on location and year uncovered the effect of photoperiod and spring temperatures in accelerating heading date in higher and lower latitudes,
Rapid Genome-Wide Location-Specific Polymorphic SSR Marker Discovery in Black Pepper by GBS Approach
Black pepper (Piper nigrum), the "King of Spices," is an economically important spice in India and is known for its medicinal and cultural values. SSRs, the tandem repeats of small DNA sequences, are often polymorphic in nature with diverse applications. For population structure, QTL/gene discovery, MAS, and diversity analysis, it is imperative to have their location specificity. The existing PinigSSRdb catalogs ~70K putative SSR markers but these are anonymous (unknown chromosomal location), based on 916 scaffolds rather than 26 chromosomes.
Photoperiod sensitivity is important for sensing seasonal changes and local adaptation. However, day-length sensitivity limits crop geographical adaptation and it should be modified during domestication. Cucumber was domesticated in southern Asia and is currently cultivated worldwide across a wide range of latitudes, but its photoperiod sensitivity and its change during cucumber domestication are unknown.
The compact architecture is a vital and valuable agronomic trait that helps to reduce the labor of plant management, and improve the fruit yield by increasing planting density in cucumbers. However, the molecular basis underlying the regulation of plant architecture in cucumber is complex and largely unknown. In this study, a novel recessive compact allele, designated as cpa-2 (compact plant architecture-2) was fine mapped in a 109 kb region on chromosome 7 by the strategy of bulked segregant analysis sequencing combined with map-based cloning
Western corn rootworm (WCR), Diabrotica virgifera virgifera, LeConte, is an insect pest that poses a significant threat to the productivity of modern agriculture, causing significant economic and crop losses. The development of genetically modified (GM) crops expressing one or more proteins that confer tolerance to specific insect pests, such as WCR, was a historic breakthrough in agricultural biotechnology and continues to serve as an invaluable tool in pest management. Despite this, evolving resistance to existing insect control proteins expressed in current generation GM crops requires continued identification of new proteins with distinct modes of action while retaining targeted insecticidal efficacy.
Land plants have developed a comprehensive system to cope with the drought stress, and it is operated by intricate signaling networks, including transcriptional regulation. Herein, we identified the function of OsNAC17, a member of NAC (NAM, ATAF, and CUC2) transcription factor family, in drought tolerance. OsNAC17 is localized to the nucleus, and its expression was significantly induced under drought conditions


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :