Desiccation tolerance is an ancient and complex trait that spans all major lineages of life on earth. Although important in the evolution of land plants, the mechanisms that underlay this complex trait are poorly understood, especially for vegetative desiccation tolerance (VDT). The lack of suitable closely related plant models that offer a direct contrast between desiccation tolerance and sensitivity has hampered progress. We have assembled high-quality genomes for two closely related grasses, the desiccation-tolerant Sporobolus stapfianus and the desiccation-sensitive Sporobolus pyramidalis. Both species are complex polyploids; S. stapfianus is primarily tetraploid, and S. pyramidalis is primarily hexaploid.
The most important viruses infecting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Brazil are BCMV, BGMV and CPMMV, the last two transmitted by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci, occurring simultaneously and causing severe yield losses. Genetically modified progenies of common bean, from carioca market class and multiple virus resistance (BCMV, BGMV and CPMMV), have been developed using conventional breeding and molecular tools. Agronomic performance and virus disease severity (VS) evaluated in two field trials, selected 39 elite progenies out of 477. Molecular analyses identified the presence of BCMV and BGMV resistance alleles in plants.
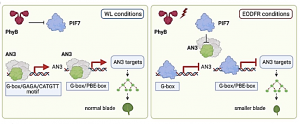
Plants are agile, plastic organisms able to adapt to everchanging circumstances. Responding to far-red (FR) wavelengths from nearby vegetation, shade-intolerant species elicit the adaptive shade-avoidance syndrome (SAS), characterized by elongated petioles, leaf hyponasty, and smaller leaves. We utilized end-of-day FR (EODFR) treatments to interrogate molecular processes that underlie the SAS leaf response. Genetic analysis established that PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 7 (PIF7) is required for EODFR-mediated constraint of leaf blade cell division, while EODFR messenger RNA sequencing data identified ANGUSTIFOLIA3 (AN3) as a potential PIF7 target.
bHLH family proteins play an important role in plant stress response. However, the molecular mechanism regulating the salt response of bHLH is largely unknown. This study aimed to investigate the function and regulating mechanism of the sweet sorghum SbbHLH85 during salt stress. The results showed that SbbHLH85 was different from its homologs in other species. Also, it was a new atypical bHLH transcription factor and a key gene for root development in sweet sorghum. The overexpression of SbbHLH85 resulted in significantly increased number and length of root hairs via ABA and auxin signaling pathways, increasing the absorption of Na+.
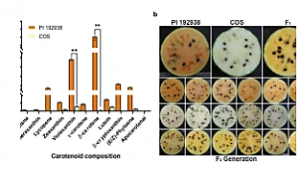
Vitamin A deficiency is a worldwide public nutrition problem, and β-carotene is the precursor for vitamin A synthesis. Watermelon with golden flesh (gf, which occurs due to an accumulated abundance of β-carotene) is an important germplasm resource. In this study, a genetic analysis of segregated gf gene populations indicated that gf was controlled by a single recessive gene. BSA-seq (Bulked segregation analysis) and an initial linkage analysis placed the gf locus in a 290-Kb region on watermelon chromosome 1. Further fine mapping in a large population including over 1000 F2 plants narrowed this region to 39.08 Kb harboring two genes, Cla97C01G008760 and Cla97C01G008770
To understand the genetic constitution of vigour in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), genomic data from a bi-parental population and multiple diversity panels were used to identify QTL, sequence-level haplotypes and genetic markers associated with vigour-related traits in Australian environments. Using 182 Recombinant Inbred Lines (RILs) derived from a cross between two desi varieties, Rupali and Genesis836, vigour QTL independent of flowering time were identified on chromosomes (Ca) 1, 3 and 4 with genotypic variance explained (GVE) ranging from 7.1 to 28.8%.
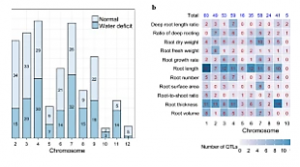
Root system architecture (RSA) is an important factor for facilitating water and nutrient uptake from deep soils and adaptation to drought stress conditions. In the present research, an integrated meta-analysis approach was employed to find candidate genes and genomic regions involved in rice RSA traits. A whole-genome meta-analysis was performed for 425 initial QTLs reported in 34 independent experiments controlling RSA traits under control and drought stress conditions in the previous twenty years. Sixty-four consensus meta-QTLs (MQTLs) were detected, unevenly distributed on twelve rice chromosomes.
Many studies have confirmed that structural variation (SV) is pervasive throughout the maize genome. Deletion is one type of SV that may impact gene expression and cause phenotypic changes in quantitative traits. In this study, two read count approaches were used to analyze the deletions in the whole-genome sequencing data of 270 maize inbred lines. A total of 19,754 deletion windows overlapped 12,751 genes, which were unevenly distributed across the genome. The deletions explained population structure well and correlated with genomic features. The deletion proportion of genes was determined to be negatively correlated with its expression.
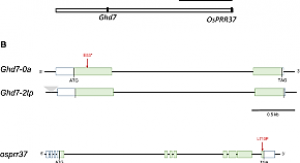
The ranges of cultivated crops expanded into various environmental conditions around the world after their domestication. Hokkaido, Japan, lies at the northern limit of cultivation of rice, which originated in the tropics. Novel genotypes for extremely early heading date in Hokkaido are controlled by loss-of-function of both Grain number, plant height and heading date 7 (Ghd7) and Oryza sativa Pseudo-Response Regulator 37 (OsPRR37). We traced genotypes for extremely early heading date and analyzed the phylogeny of rice varieties grown historically in Japan.
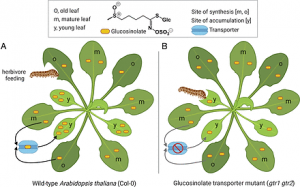
Plants, as a whole, are well stocked with chemical defense compounds that function in protection against herbivores and pathogens. Within individual plants, however, there is extensive variation in the amounts of chemical defenses among different organs, tissues, and developmental stages. For example, defense compounds are typically present in greater concentrations in young compared to old leaves and in reproductive compared to vegetative organs. These patterns have been rationalized by various theories, chief among them the optimal defense theory, but this theory has proved very difficult to test until a recent report from Hunziker et al. (1).


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :