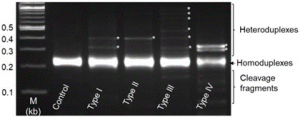
Phytophthora sojae is the causative agent for Phytophthora root and stem rot in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] and can be managed by deployment of resistance to P. sojae (Rps) genes. PI 340,029 is a soybean landrace carrying broad-spectrum resistance to the pathogen. Analysis of an F2 population derived from a cross between PI 340,029 and a susceptible cultivar ‘Williams’ reveals that the resistance to P. sojae race 1 is conferred by a single gene,
Jasmonate signaling for adaptative or developmental responses generally relies on an increased synthesis of the bioactive hormone jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile), triggered by environmental or internal cues. JA-Ile is embedded in a complex metabolic network whose upstream and downstream components strongly contribute to hormone homeostasis and activity. We previously showed that JAO2, an isoform of four Arabidopsis JASMONIC ACID OXIDASES,
Transcription activator-like effector (TALE) nucleases (TALENs) mediated gene editing methods are becoming popular and have revealed the staggering complexity of genome control during development. Here, we present a simple and efficient gene knockout using TALENs in kawakawa, Euthynnus affinis, using slc24a5. We examined slc24a5 gene expression and functional differences between two TALENs that hold the TALE scaffolds, +153/+47 and +136/+63 and target slc24a5
Rice is a key food security crop in Africa. The importance of rice has led to increasing country-specific, regional, and multinational efforts to develop germplasm and policy initiatives to boost production for a more food-secure continent. Currently, this critically important cereal crop is predominantly cultivated by small-scale farmers under suboptimal conditions in most parts of sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).
Selection indices using genomic information have been proposed in crop-specific scenarios. Routine use of genomic selection (GS) for simultaneous improvement of multiple traits requires information about the impact of the available economic and logistic resources and genetic properties (variances, trait correlations, and prediction accuracies) of the breeding population on the expected selection gain. We extended the R package “selectiongain” from single trait to index selection to optimize and compare breeding strategies for simultaneous improvement of two traits.
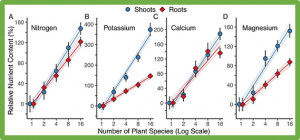
Fertile soils have been an essential resource for humanity for 10,000 y, but the ecological mechanisms involved in the creation and restoration of fertile soils, and especially the role of plant diversity, are poorly understood. Here we use results of a long-term, unfertilized plant biodiversity experiment to determine whether biodiversity, especially plant functional biodiversity, impacted the regeneration of fertility on a degraded sandy soil. After 23 y, plots containing 16 perennial grassland plant species had, relative to monocultures of these same species, ∼30 to 90% greater increases in soil nitrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, cation exchange capacity, and carbon and had ∼150 to 370% greater amounts of N, K, Ca, and Mg in plant biomass.
Camelina sativa (camelina) is emerging as an alternative oilseed crop due to its short growing cycle, low input requirements, adaptability to less favorable growing environments and a seed oil profile suitable for biofuel and industrial applications. Camelina meal and oil are also registered for use in animal and fish feeds; however, like meals derived from most cereals and oilseeds, it is deficient in certain essential amino acids, such as lysine.
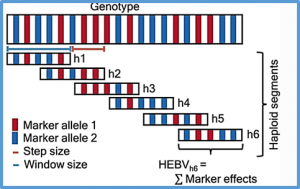
Genomic prediction is often combined with truncation selection to identify superior parental individuals that can pass on favorable quantitative trait locus (QTL) alleles to their offspring. However, truncation selection reduces genetic variation within the breeding population, causing a premature convergence to a sub-optimal genetic value. In order to also increase genetic gain in the long term, different methods have been proposed that better preserve genetic variation.
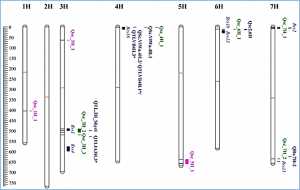
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) of four Multi-parent Advanced Generation Inter-Cross (MAGIC) populations identified nine regions on chromosomes 1H, 3H, 4H, 5H, 6H and 7H associated with resistance against barley scald disease. Three of these regions are putatively novel resistance Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL). Barley scald is caused by Rhynchosporium commune, one of the most important barley leaf diseases that are prevalent in most barley-growing regions.
Structural variations (SVs), such as inversion and duplication, contribute to important agronomic traits in crops1. Pan-genome studies revealed that SVs were a crucial and ubiquitous force driving genetic diversification 2,3,4. Although genome editing can effectively create SVs in plants and animals 5,6,7,8, the potential of designed SVs in breeding has been overlooked. Here, we show that new genes and traits can be created in rice by designed large-scale genomic inversion or duplication using CRISPR/Cas9.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :