| Pinpointing genomic regions associated with root system architecture in rice through an integrative meta-analysis approach |
|
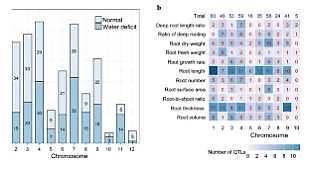
Root system architecture (RSA) is an important factor for facilitating water and nutrient uptake from deep soils and adaptation to drought stress conditions. In the present research, an integrated meta-analysis approach was employed to find candidate genes and genomic regions involved in rice RSA traits. A whole-genome meta-analysis was performed for 425 initial QTLs reported in 34 independent experiments controlling RSA traits under control and drought stress conditions in the previous twenty years. Sixty-four consensus meta-QTLs (MQTLs) were detected, unevenly distributed on twelve rice chromosomes. |
|
Theoretical and Applied Genetics, January 2022; vol. 135: 81–106
Key messageApplying an integrated meta-analysis approach led to identification of meta-QTLs/ candidate genes associated with rice root system architecture, which can be used in MQTL-assisted breeding/ genetic engineering of root traits. AbstractRoot system architecture (RSA) is an important factor for facilitating water and nutrient uptake from deep soils and adaptation to drought stress conditions. In the present research, an integrated meta-analysis approach was employed to find candidate genes and genomic regions involved in rice RSA traits. A whole-genome meta-analysis was performed for 425 initial QTLs reported in 34 independent experiments controlling RSA traits under control and drought stress conditions in the previous twenty years. Sixty-four consensus meta-QTLs (MQTLs) were detected, unevenly distributed on twelve rice chromosomes. The confidence interval (CI) of the identified MQTLs was obtained as 0.11–14.23 cM with an average of 3.79 cM, which was 3.88 times narrower than the mean CI of the original QTLs. Interestingly, 52 MQTLs were co-located with SNP peak positions reported in rice genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for root morphological traits. The genes located in these RSA-related MQTLs were detected and explored to find the drought-responsive genes in the rice root based on the RNA-seq and microarray data. Multiple RSA and drought tolerance-associated genes were found in the MQTLs including the genes involved in auxin biosynthesis or signaling (e.g. YUCCA, WOX, AUX/IAA, ARF), root angle (DRO1-related genes), lateral root development (e.g. DSR, WRKY), root diameter (e.g. OsNAC5), plant cell wall (e.g. EXPA), and lignification (e.g. C4H, PAL, PRX and CAD). The genes located within both the SNP peak positions and the QTL-overview peaks for RSA are suggested as novel candidate genes for further functional analysis. The promising candidate genes and MQTLs can be used as basis for genetic engineering and MQTL-assisted breeding of root phenotypes to improve yield potential, stability and performance in a water-stressed environment.
See https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00122-021-03953-5 |
|
|
|
[ Tin tức liên quan ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :