Heat stress impacts the quantity and quality of rice grains, particularly during grain-flling stage needed for grain development. In this study, the effect of short heat stress (42 °C, 30 min) on indica rice plants at the grain-flling stage (dough grain stage) was found by determining their physiological and growth traits Fv/Fm, ∆F/Fm′, chlorophyll content, leaf water potential (LWP), membrane stability, relative leaf area (RLA), relative plant height (RPH), total grain weight per panicle (TGW) and 1000 GW.
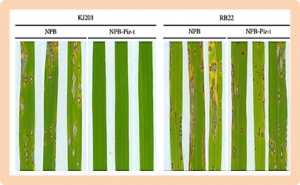
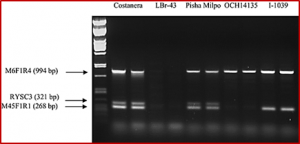
Rice blast (caused by Magnaporthe oryzae) is one of the most destructive diseases of rice. While many blast resistance (R) genes have been identified and deployed in rice cultivars, little is known about the R gene-mediated defense mechanism. We used a rice transgenic line harboring the resistance gene Piz-t to investigate the R gene-mediated resistance response to infection.
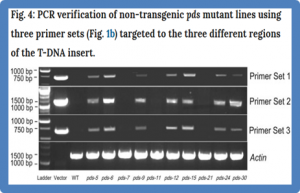
Developing CRISPR/Cas9-mediated non-transgenic mutants in asexually propagated perennial crop plants is challenging but highly desirable. Here, we report a highly useful method using an Agrobacterium-mediated transient CRISPR/Cas9 gene expression system to create non-transgenic mutant plants without the need for sexual segregation. We have also developed a rapid, cost-effective, and high-throughput mutant screening protocol based on Illumina sequencing followed by high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis
Capsaicinoids are unique compounds produced only in peppers (Capsicum spp.). Several studies using classical quantitative trait loci (QTLs) mapping and genomewide association studies (GWAS) have identified QTLs controlling capsaicinoid content in peppers; however, neither the QTLs common to each population nor the candidate genes underlying them have been identified due to the limitations of each approach used. Here, we performed QTL mapping and GWAS for capsaicinoid content in peppers using two recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations and one GWAS population.
Here we describe a method for robust directed evolution using mutagenesis of large sequence spaces in their genomic contexts. The method employs error-prone PCR and Cas9-mediated genome integration of mutant libraries of large-sized donor variants into single or multiple genomic sites with efficiencies reaching 98–99%.
The obligate biotrophic fungus Podosphaera aphanis is the causative agent of powdery mildew on cultivated strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa). Genotypes from two bi-parental mapping populations ‘Emily’בFenella’ and ‘Redgauntlet’בHapil’ were phenotyped for powdery mildew disease severity in a series of field trials. Here, we report multiple QTL associated with resistance to powdery mildew, identified in ten phenotyping events conducted across different years and locations.
Phosphorus (P) is the essential macro-element supporting rice productivity. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) underlying related traits at the seedling stage under two different phosphorus levels was investigated in rice using a population of 76 Chromosomal Sequence Substitution Lines (CSSLs) derived from a cross between the maintainer variety XieqingzaoB (P stress tolerant) and the restorer variety Zhonghui9308 (P stress sensitive); the parents of super hybrid rice Xieyou9308.
Potato virus Y (PVY) is causing yield and quality losses forcing farmers to renew periodically their seeds from clean stocks. Two loci for extreme resistance to PVY, one on chromosome XI and the other on XII, have been identified and used in breeding. The latter corresponds to a well-known source of resistance (Solanum stoloniferum), whereas the one on chromosome XI was reported from S. stoloniferum and S. tuberosum group Andigena as well
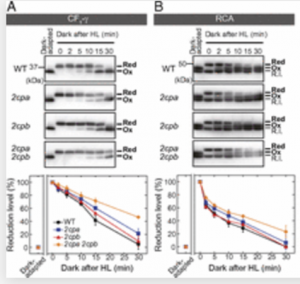
To ensure efficient photosynthetic carbon gain, plant chloroplasts have to adjust their own physiology toward changes in light environments. Specific chloroplast proteins are reversibly activated–inactivated during light–dark cycles by switching the reduction–oxidation states of their Cys residues, which is termed redox regulation. A long-standing issue in plant biology is the manner in which redox-regulated proteins are reoxidized upon the interruption of light exposure.
Root systems play important roles in crop growth and stress responses. Although genetic mechanism of root traits in maize (Zea mays L.) has been investigated in different mapping populations, root traits have rarely been utilized in breeding programs. Elucidation of the genetic basis of maize root traits and, more importantly, their connection to other agronomic trait(s), such as grain yield, may facilitate root trait manipulation and maize germplasm improvement


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :