With pectoral fins that surround much of the body, by fusing to the head, the skate is a cartilaginous fish that has one of the most unique appendages of all vertebrates. Here, we use an unbiased RNA screen to uncover genetic pathways underlying this morphology. Unlike tetrapods and other fishes, skates induce a second growth center in the anterior region, by the redeployment of an ancient genetic module.
Molecular confirmation of interspecific recombinants is essential to overcome the issues like self-pollination, environmental influence, and inadequacy of morphological characteristics during interspecific hybridization. The present study was conducted for genetic confirmation of mungbean (female) and mashbean (male) interspecific crosses using molecular markers. Initially, polymorphic random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), universal rice primers (URP), and simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers differentiating parent genotypes were identified.
Soybean is a major source of protein and oil and a primary feedstock for biodiesel production. Research on soybean seed composition and yield has revealed that protein, oil and yield are controlled quantitatively and quantitative trait loci (QTL) have been identified for each of these traits. However, very limited information is available regarding the genetic mechanisms controlling seed composition and yield.
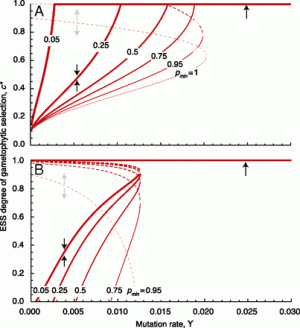
Diploid organisms manipulate the extent to which their haploid gametes experience selection. Animals typically produce sperm with a diploid complement of most proteins and RNA, limiting selection on the haploid genotype. Plants, however, exhibit extensive expression in pollen, with actively transcribed haploid genomes. Here we analyze models that track the evolution of genes that modify the strength of haploid selection to predict when evolution intensifies and when it dampens the “selective arena” within which male gametes compete for fertilization.
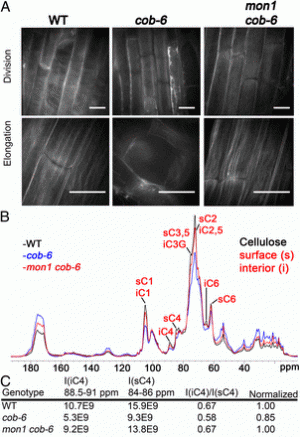
The cobra mutants of Arabidopsis, such as cob-6, have impaired growth associated with a defect in cellulose synthesis. Mutations in MEDIATOR16 (MED16) reduce the number of misregulated genes in cob-6 mutants and suppress the phenotypes. This observation implicates MED16 in transcriptional responses to cell wall defects. Ectopic expression of two pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEIs) identified in a suppressor screen partially suppressed the growth defect in the cob-6 mutant.
It is widely accepted that the 14-3-3 family proteins are key regulators of multiple stress signal transduction cascades. By conducting genome-wide analysis, researchers have identified the soybean 14-3-3 family proteins; however, until now, there is still no direct genetic evidence showing the involvement of soybean 14-3-3s in ABA responses. Hence, in this study, based on the latest Glycine max genome on Phytozome v10.3, we initially analyzed the evolutionary relationship, genome organization, gene structure and duplication, and three-dimensional structure of soybean 14-3-3 family proteins systematically.
Significant progress has been achieved in our understanding of plant adaptive responses to ensure growth and reproduction in soils with low phosphate (Pi) availability. However, the potential role of epigenetic mechanisms in the modulation of these responses remains largely unknown. In this article, we describe dynamic changes in global DNA methylation patterns that occur in Arabidopsis plants exposed to low Pi availability; these changes are associated with the onset of Pi starvation responses.
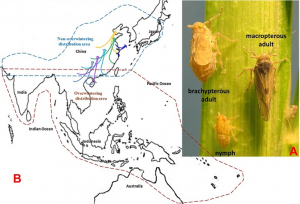
Many plant-parasite interactions that include major plant resistance genes have subsequently been shown to exhibit features of gene-for-gene interactions between plant Resistance genes and parasite Avirulence genes. The brown planthopper (BPH) Nilaparvata lugens is an important pest of rice (Oryza sativa). Historically, major Resistance genes have played an important role in agriculture. As is common in gene-for-gene interactions, evolution of BPH virulence compromises the effectiveness of singly-deployed resistance genes
The brown plant hopper is one of the most destructive known pests of rice. We studied the roles of the JH receptor Met and the downstream transcription factor Kr-h1 in ovariole development and egg maturation. The predicted Met protein in N. lugens (NlMet) contained 517 amino acids. qRT-PCR showed that NlMet was expressed in all tissues and that the highest expression occurred in the embryonic stage. In NlMet- or NlKr-h1-silenced female adults, ovarian development varied significantly
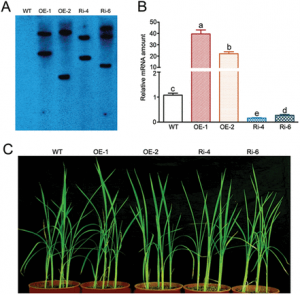
The WRKY transcription factor family has 109 members in the rice genome, and has been reported to be involved in the regulation of biotic and abiotic stress in plants. Here, we demonstrated that a rice OsWRKY74 belonging to group III of the WRKY transcription factor family was involved in tolerance to phosphate (Pi) starvation. OsWRKY74 was localized in the nucleus and mainly expressed in roots and leaves.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :