Cassava is an important food and potential biofuel crop that is tolerant to multiple abiotic stressors. The mechanisms underlying these tolerances are currently less known. CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) have been shown to play crucial roles in plant developmental processes, hormone signaling transduction, and in the response to abiotic stress. However, no data is currently available about the CPK family in cassava. In this study, a total of 25 CIPK genes were identified from cassava genome based on our previous genome sequencing data.
This study was to investigate the effect of soyabean isoflavones (SIF) on onset of puberty, serum hormone concentration, and gene expression in hypothalamus, pituitary and ovary of female Bama miniature pigs. Fifty five, 35-days old pigs were randomly assigned into 5 treatment groups consisting of 11 pigs per treatment.
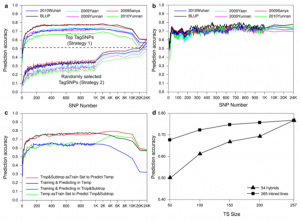
Kernel row number (KRN) is an important yield component in maize and directly affects grain yield. In this study, we combined linkage and association mapping to uncover the genetic architecture of maize KRN and to evaluate the phenotypic predictability using these detected loci. A genome-wide association study revealed 31 associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) representing 17 genomic loci with an effect in at least one of five individual environments and the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) over all environments
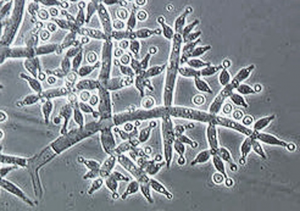
The expression of antifungal genes from Trichoderma harzianum (figure), mainly chitinases, has been used to confer plant resistance to fungal diseases. However, the biotechnological potential of glucanase genes from Trichoderma has been scarcely assessed. In this research, transgenic strawberry plants expressing the β-1,3-glucanase gene bgn13.1 from T. harzianum, under the control of the CaMV35S promoter, have been generated. After acclimatization, five out of 12 independent lines analysed showed a stunted phenotype when growing in the greenhouse.
Regulators of chromatin structure play critical roles in DNA-based processes. Lysine (K) Methyltransferase 1 (KMT1) homologs perform methylation of H3 lysine-9 and are best known for their essential role in heterochromatin formation and transcriptional silencing. Heterochromatin formation is also important for maintenance of genome stability, although the mechanisms are not well understood.
Magnaporthe oryzae is the causal agent of rice blast disease, the most devastating disease of cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) and a continuing threat to global food security. To cause disease, the fungus elaborates a specialized infection cell called an appressorium, which breaches the cuticle of the rice leaf, allowing the fungus entry to plant tissue. Here, we show that the exocyst complex localizes to the tips of growing hyphae during vegetative growth.
Plants can sense loss of water caused by drought and stimulate internal mechanisms for protecting cells from damage with the aid of the stress hormone abscisic acid (ABA). Analysis of a mutant of the basal land plant, the moss Physcomitrella patens, revealed that an impairment of a protooncogene Raf-like protein kinase, designated “ARK” (for “ABA and abiotic stress-responsive Raf-like kinase”),
Pathogen infections can cause significant crop losses worldwide and major disturbances in natural ecosystems. Understanding the molecular basis of plant disease susceptibility is important for the development of new strategies to prevent disease outbreaks. Recent studies have identified the plant jasmonate (JA) hormone receptor as one of the common targets of pathogen virulence factors.
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) closes its stomata at relatively low soil water deficits frequently encountered in normal field conditions resulting in unnecessary annual yield losses and extensive use of artificial irrigation. Therefore, unraveling the genetics underpinning variation in water use efficiency (WUE) of potato is important, but has been limited by technical difficulties in assessing the trait on individual plants and thus is poorly understood.
TaNAC29 was introduced into Arabidopsis using the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated floral dipping method. TaNAC29-overexpression plants were subjected to salt and drought stresses for examining gene functions. To investigate tolerant mechanisms involved in the salt and drought responses, expression of related marker genes analyses were conducted, and related physiological indices were also measured. Expressions of genes were analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :