SWEET (MtN3_saliva) domain proteins, a recently identified group of efflux transporters, play an indispensable role in sugar efflux, phloem loading, plant-pathogen interaction and reproductive tissue development. The SWEET gene family is predominantly studied in Arabidopsis and members of the family are being investigated in rice. To date, no transcriptome or genomics analysis of soybean SWEET genes has been reported.
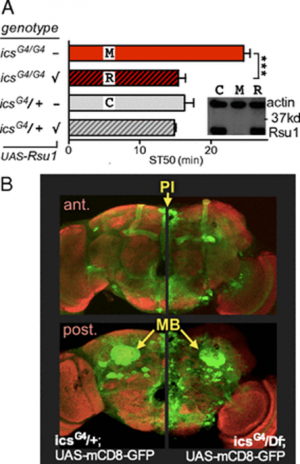
Genetic factors play a major role in the development of human addiction. Identifying these genes and understanding their molecular mechanisms are necessary first steps in the development of targeted therapeutic intervention. Here, we have isolated the gene encoding Ras suppressor 1 (Rsu1) in an unbiased genetic screen for altered ethanol responses in the vinegar fly, Drosophila melanogaster.
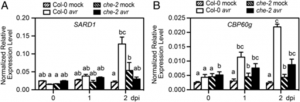
Biosynthesis of the plant immune signal salicylic acid (SA) is normally induced upon pathogen challenge through transcriptional activation of the key SA synthetic enzyme gene, ICS1. However, how different pathogenic signals trigger SA synthesis in both local and systemic tissues and during different immune responses is poorly understood
The study of natural variation has profoundly advanced our understanding of plants’ phenotypic trait evolution. The analysis of intraspecific variations in metabolism, however, has lagged behind and frequently been biased toward central metabolism. To redress this bias, we present a metabolomics case study of leaf secondary metabolites of wild tobacco ecotypes subjected to simulated insect herbivory in which mass spectral maps are constructed.
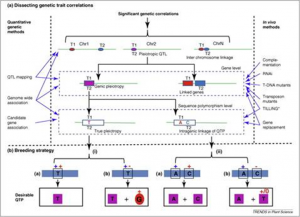
Plant height is one of the most heritable traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Understanding the genetic control of plant height is important for elucidating the molecular mechanisms that regulate maize development. To investigate the genetic basis of the plant height response to density in maize, we evaluated the effects of two different plant densities (60,000 and 120,000 plant/hm2) on three plant height-related traits (plant height, ear height, and ear height-to-plant height ratio) using four sets of recombinant inbred line populations.
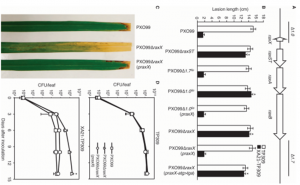
Surveillance of the extracellular environment by immune receptors is of central importance to eukaryotic survival. ThericereceptorkinaseXA21,whichconfers robust resistance to most strains of the Gram-negative bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo), is representative of a large class of cell surface immune receptors in plants and animals. We report the identification of a previously undescribed Xoo protein, called RaxX, which is required for activation of XA21-mediated immunity.
Black raspberry (Rubus occidentalis L.) is a high-value crop in the Pacific Northwest of North America with an international marketplace. Few genetic resources are readily available and little improvement has been achieved through breeding efforts to address production challenges involved in growing this crop. Contributing to its lack of improvement is low genetic diversity in elite cultivars and an untapped reservoir of genetic diversity from wild germplasm.
A significant fraction of the length of Escherichia coli genomes comprises mobile elements integrated at various sites in a ∼4-Mbp basic genome shared by the species. We find that the entire basic genome is continually exchanged by homologous recombination with genome fragments acquired from other genomes in the population. Evolutionary groups appear to exchange DNA preferentially within the same group but also with other groups to different extents.
Aflatoxin-producing fungi can contaminate plants and plant-derived products with carcinogenic secondary metabolites that present a risk to human and animal health. In this study, we investigated the effect of antimicrobial peptides on the major aflatoxigenic fungi Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus. In vitro assays with different chemically-synthesized peptides demonstrated that the broad-spectrum peptide thanatin from the spined soldier bug (Podisus maculiventris) had the greatest potential to eliminate aflatoxigenic fungi.
The Trp triad-dependent photoreduction of the flavin chromophore has been widely accepted as the photoexcitation mechanism of cryptochrome photoreceptors. However, the experimental evidence supporting this hypothesis derived primarily from the biophysical studies in vitro, except for one genetics study of Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 (CRY1). In contrast to the previous report,


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :