Recent calls to establish a global project registry before releasing any gene-drive-modified organisms (GDOs) have suggested a registry could be valuable to coordinate research, collect data to monitor and evaluate potential ecological impacts, and facilitate transparent communication with community stakeholders and the general public. Here, we report the results of a multidisciplinary expert workshop on GDO registries convened on 8–9 December 2020 involving 70 participants from 14 countries.
The genetic diversity provided by subgenome homoeologs in allopolyploid wheat can be leveraged for developing improved wheat varieties with modified chemical traits, including profiles of carotenoids, which play critical roles in photosynthesis, photoprotection, and growth regulation. Carotenoid profiles are greatly influenced by hydroxylation catalyzed by β-hydroxylases (HYDs). To genetically dissect the contribution of HYDs to carotenoid metabolism and wheat growth and yield,
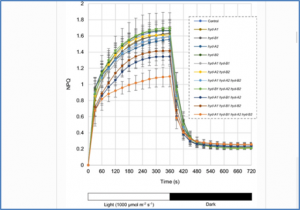
Phosphorus (P) is a macronutrient required for plant growth and reproduction. Orthophosphate (Pi), the preferred P form for plant uptake, is easily fixed in the soil, making it unavailable to plants. Limited phosphate rock resources, low phosphate fertilizer use efficiency and high demands for green agriculture production make it important to clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying plant responses to P deficiency and to improve plant phosphate efficiency in crops. Over the past 20 years, tremendous progress has been made in understanding the regulatory mechanisms of the plant P starvation response.
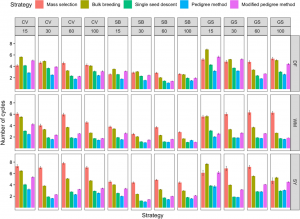
Dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) are a nutrient dense legume that is consumed by developed and developing nations around the world. The progress to improve this crop has been quite steady. However, with the continued rise in global populations, there are demands to expedite genetic gains. Plant breeders have been at the forefront at increasing yields in the common bean. As breeding programs are both time-consuming and resource intensive, resource allocation must be carefully considered. To assist plant breeders, computer simulations can provide useful information that may then be applied to the real world.
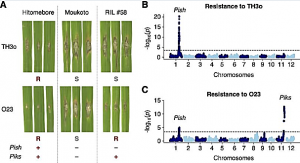
Studies focused solely on single organisms can fail to identify the networks underlying host-pathogen gene-for-gene interactions. Here, we integrate genetic analyses of rice (Oryza sativa, host) and rice blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae, pathogen) and uncover a new pathogen recognition specificity of the rice nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein (NLR) immune receptor Pik, which mediates resistance to M. oryzae expressing the avirulence effector gene AVR-Pik. Rice Piks-1, encoded by an allele of Pik-1, recognizes a previously unidentified effector encoded by the M. oryzae avirulence gene AVR-Mgk1, which is found on a mini-chromosome.
Powdery mildew (PM) is one of the most destructive fungal diseases of melon, which significantly reduces the crop yield and quality. Multiple studies are being performed for in-depth genetic understandings of PM-susceptibility or -resistance mechanisms in melon plants, but the holistic knowledge of the precise genetic basis of PM-resistance is unexplored. In this study, we characterized the recessive gene “Cmpmr2F” and found its association with resistance against the PM causative agent “Podosphaera xanthii race 2F.” Fine genetic mapping revealed the major-effect region of a 26.25-kb interval on chromosome 12, which harbored the Cmpmr2F gene corresponding to the MELO3C002403, encoding allantoate amidohydrolase.
Transgene escape could lead to genetically modified rice establishing wild populations in the natural environment, where they would compete for survival space with weeds. However, whether the expression of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) gene in rice will alter the relationship between transgene plants and weeds and induce undesirable environmental consequences are poorly understood. Thus, field experiments were conducted to investigate the weed competitiveness and assess the ecological risk of transgenic Bt rice under herbicide-free and lepidopterous pest controlled environment.
Broad-spectrum disease resistance genes are desirable in crop breeding for conferring stable, durable resistance in field production. Pm21(4#) is a gene introduced from wild Haynaldia villosa into wheat that confers broad-spectrum resistance to wheat powdery mildew and has been widely used in wheat production for approximately 30 years. The discovery and transfer of new functional haplotypes of Pm21 into wheat will expand its genetic diversity in production and avoid the breakdown of resistance conferred by a single gene on a large scale.
Genetically modified (GM) crops tolerant to glyphosate have delivered significant economic benefits in farm management. However, the evolution of glyphosate resistance in weeds due to prolonged intensive use of glyphosate poses a serious threat to this weed management system. It is highly desirable in China to deploy dual herbicide-tolerant corn at the very beginning of GM corn release to delay the development of weed resistance to herbicides. Here, we report the creation and characterization of a herbicide-tolerant corn event SCB-29 that expresses both cp4 epsps and bar genes.
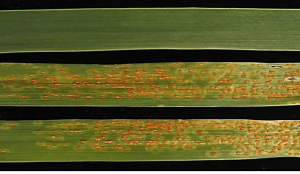
Leaf rust (Puccinia triticina) is one of the most devastating fungal diseases of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Discovery and identification of new resistance genes is essential to develop disease-resistant cultivars. An advanced breeding line Yang16G216 was previously identified to confer adult-plant resistance (APR) to leaf rust. In this research, a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population was constructed from the cross between Yang16G216 and a highly susceptible line Yang16M6393, and genotyped with exome capture sequencing and 55 K SNP array.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :