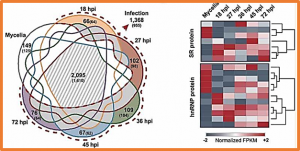
Alternative splicing (AS) contributes to diversifying and regulating cellular responses to environmental conditions and developmental cues by differentially producing multiple mRNA and protein isoforms from a single gene. Previous studies on AS in pathogenic fungi focused on profiling AS isoforms under a limited number of conditions. We analysed AS profiles in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, a global threat to rice production, using high-quality transcriptome data representing its vegetative growth (mycelia) and multiple host infection stages
During plant-pathogenic fungi and host plants interactions, numerous pathogen-derived proteins are secreted resulting in the activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. For efficient trafficking of secretory proteins, including those important in disease progression, the cytoplasmic coat protein complex II (COPII) exhibits a multifunctional role whose elucidation remains limited.
In order to understand the molecular mechanism of cotton's response to drought during the flowering and boll stage, transcriptomics and metabolomics were carried out for two introgression lines (drought-tolerant line: T307; drought-sensitive line: S48) which were screened from Gossypium hirsutum cv. ‘Emian22’ with some gene fragments imported from Gossypium barbadense acc. 3–79, under drought stress by withdrawing water at flowering and boll stage.
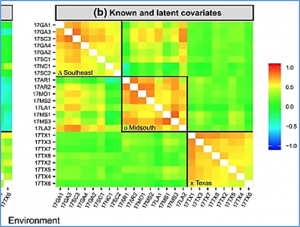
This paper develops a single-stage genomic selection approach which integrates known and latent environmental covariates within a special factor analytic framework. The factor analytic linear mixed model of Smith et al. (2001) is an effective method for analysing multi-environment trial (MET) datasets, but has limited practicality since the underlying factors are latent so the modelled genotype by environment interaction (GEI) is observable, rather than predictable.
Grain size is an important agronomic trait determining grain yield and appearance quality in rice. Here, we report the discovery of rice mutant short and narrow grain1 (sng1) with reduced grain length, width and weight. Map-based cloning revealed that the mutant phenotype was caused by loss of function of gene OsHXK3 that encodes a hexokinase-like (HKL) protein. OsHXK3 was associated with the mitochondria and was ubiquitously distributed in various organs, predominately in younger organs.
Watermelon is a xerophytic crop characterized by a long primary root and robust lateral roots. Therefore, watermelon serves as an excellent model for studying root elongation and development. However, the genetic mechanism underlying the primary root elongation in watermelon remains unknown. Herein, through bulk segregant analysis we identified a genetic locus, qPRL.Chr03, controlling primary root length (PRL) using two different watermelon species (Citrullus lanatus and Citrullus amarus) that differ in their root architecture.
The application of a male-sterile line is an ideal approach of hybrid seed production in Chinese cabbage. In this study, we obtained a male-sterile mutant (ftms1) from the double haploid line ‘FT’ using ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS) mutagenesis. The mutant was completely sterile due to abnormal enlargement and vacuolization of the tapetum cells. A single recessive nuclear gene was found to control male sterility in the mutant, while MutMap and KASP analyses identified BraA05g022470.3C (BrGGL7),
The extent to which horizontal gene transfer (HGT) has shaped eukaryote evolution remains an open question. Two recent studies reported four plant-like genes acquired through two HGT events by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci, a major agricultural pest (Lapadula et al. 2020; Xia et al. 2021). Here, we uncovered a total of 49 plant-like genes deriving from at least 24 independent HGT events in the genome of the MEAM1 whitefly. Orthologs of these genes are present in three cryptic B. tabaci species, they are phylogenetically nested within plant sequences, and expressed and under purifying selection
Salt stress is one of the most severe adverse environments in rice production; increasing salinization is seriously endangering rice production around the world. In this study, a rice backcross inbred line (BIL) population derived from the cross of 9311 and wild rice Oryza longistaminata was employed to identify the favorable genetic loci of O. longistaminata for salt tolerance. A total of 27 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to salt tolerance were identified in 140 rice BILs
Salt stress is a major constraint on plant growth and yield. Nitrogen (N) fertilizers are known to alleviate salt stress. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we show that nitrate-dependent salt tolerance is mediated by OsMADS27 in rice. The expression of OsMADS27 is specifically induced by nitrate. The salt-inducible expression of OsMADS27 is also nitrate-dependent.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :