Grain yield (GY) production can be expressed as the result of three main efficiencies: light interception (Ei), radiation use (RUE), and harvest index (HI). Although dissecting GY through these three efficiencies is not entirely new, there is a lack of knowledge about the phenotypic variation, the genetic architecture, and the relative contribution of these three efficiencies on GY in soybean. This knowledge gap coupled with laborious phenotyping prevents the active consideration of these efficiencies into breeding programs.
Rice blast, caused by Magnaporthe oryzae, is one of the most devastating diseases in rice and can affect rice production worldwide. Rice plasma membrane (PM) proteins are crucial for rapidly and precisely establishing a defense response in plant immunity when rice and blast fungi interact. However, the plant-immunity-associated vesicle trafficking network mediated by PM proteins is poorly understood. In this study, to explore changes in PM proteins during M. oryzae infection
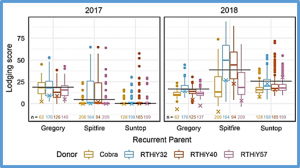
Lodging is a barrier to achieving high yield in wheat. As part of a study investigating the potential to breed low-lodging high-yielding wheat, populations were developed crossing four low-lodging high-yielding donors selected based on lodging related traits, with three cultivars. Lodging was evaluated in single rows in an early generation and subsequently in plots in 2 years with contrasting lodging environment.
Genotype imputation is a strategy to increase marker density of existing datasets without additional genotyping. We compared imputation performance of software BEAGLE 5.0, IMPUTE 5 and AlphaPlantImpute and tested software parameters that may help to improve imputation accuracy in soybean populations. Several factors including marker density, extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD), minor allele frequency (MAF), etc.
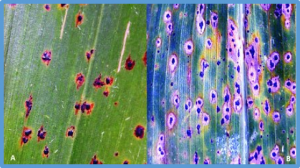
Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) is widely consumed and cultivated in the world. Gray leaf spot (GLS), caused by Stemphylium lycopersici (S. lycopersici), is one of the most devastating diseases in tomato production. To date, only one resistance gene, Sm, which confers high resistance against GLS disease, has been identified in the wild tomato species Solanum pimpinellifolium. This resistance locus (comprising the Sm gene) has been transferred into the cultivated variety ‘Motelle’.
Sugarcane, with its exceptional carbon dioxide assimilation, biomass and sugar yield, has a high potential for the production of bio-energy, bio-plastics and high-value products in the food and pharmaceutical industries. A crucial challenge for long-term economic viability and environmental sustainability is also to optimize the production of biomass composition and carbon sequestration. Sugarcane varieties such as KQ228 and Q253 are highly utilized in the industry.
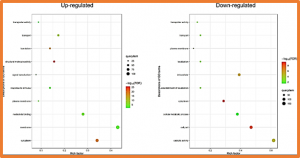
Tar spot complex (TSC) is a major foliar disease of maize in many Central and Latin American countries and leads to severe yield loss. To dissect the genetic architecture of TSC resistance, a genome-wide association study (GWAS) panel and a bi-parental doubled haploid population were used for GWAS and selective genotyping analysis, respectively. A total of 115 SNPs in bin 8.03 were detected by GWAS and three QTL in bins 6.05, 6.07, and 8.03 were detected by selective genotyping.
Meiotic recombination is a biological process of key importance in breeding, to generate genetic diversity and develop novel or agronomically relevant haplotypes. In crop tomato, recombination is curtailed as manifested by linkage disequilibrium decay over a longer distance and reduced diversity compared with wild relatives. Here, we compared domesticated and wild populations of tomato and found an overall conserved recombination landscape, with local changes in effective recombination rate in specific genomic regions.
Flowering is a critical agricultural trait that substantially affects tomato fruit yield. Although drought stress influences flowering time, the molecular mechanism underlying drought-regulated flowering in tomato remains elusive. In this study, we demonstrated that loss of function of tomato OPEN STOMATA 1 (SlOST1), a protein kinase essential for abscisic acid (ABA) signaling and abiotic stress responses, lowers the tolerance of tomato plants to drought stress. slost1 mutants also exhibited a late flowering phenotype under both normal and drought stress conditions.
We analyze loss-of-function mutants of two major genes encoding DNA demethylases. No significant change in DNA methylation has been detected in these mutants. However, we detect increased DNA methylation levels in the mutants around genes and some transposons. The increase in DNA methylation is accompanied by alteration in gene expression, with a tendency to show downregulation, especially for the genes that are preferentially expressed in endosperm


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :