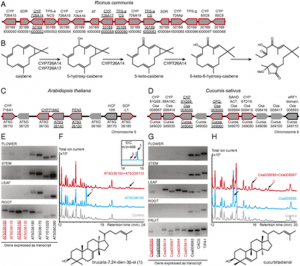
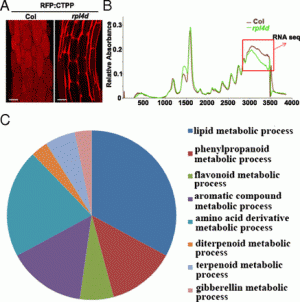
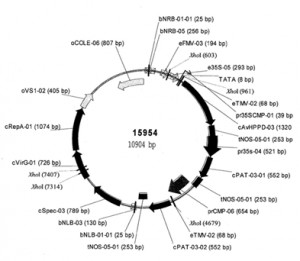
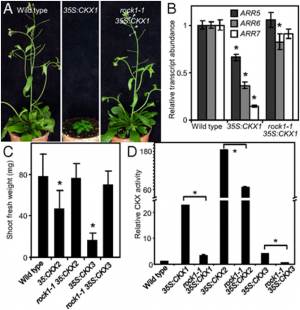
|
Critical roles of DNA demethylation in the activation of ripening-induced genes and inhibition of ripening-repressed genes in tomato fruit
Thursday, 2017/06/01 | 07:41:37
|
Critical roles of DNA demethylation in the activation of ripening-induced genes and inhibition of ripening-repressed genes in tomato fruit
Zhaobo Lang, Yihai Wang, Kai Tang, Dengguo Tang, Tatsiana Datsenka, Jingfei Cheng, Yijing Zhang, Avtar K. Handa, and Jian-Kang Zhu
Significance
DNA methylation is generally considered an epigenetic mark for transcriptional gene silencing. In this work, we generated loss-of-function mutant alleles of SlDML2. We characterized the mutant fruits that failed to ripen and discovered that SlDML2 is required for the demethylation and activation of genes important for fruit ripening, including genes involved in fruit pigment and flavor synthesis, ethylene synthesis and signaling, and cell wall hydrolysis. Unexpectedly, we found that SlDML2-mediated DNA demethylation is also necessary for fruit ripening-induced repression of hundreds of genes involved in photosynthesis and cell wall synthesis and organization. Our study has therefore revealed a broad and critical role of DNA methylation as an activation mark for the expression of many genes in a eukaryotic organism.
Abstract
DNA methylation is a conserved epigenetic mark important for genome integrity, development, and environmental responses in plants and mammals. Active DNA demethylation in plants is initiated by a family of 5-mC DNA glycosylases/lyases (i.e., DNA demethylases). Recent reports suggested a role of active DNA demethylation in fruit ripening in tomato. In this study, we generated loss-of-function mutant alleles of a tomato gene, SlDML2, which is a close homolog of the Arabidopsis DNA demethylase gene ROS1. In the fruits of the tomato mutants, increased DNA methylation was found in thousands of genes. These genes included not only hundreds of ripening-induced genes but also many ripening-repressed genes. Our results show that SlDML2 is critical for tomato fruit ripening and suggest that active DNA demethylation is required for both the activation of ripening-induced genes and the inhibition of ripening-repressed genes.
See: http://www.pnas.org/content/114/22/E4511.abstract.html?etoc
PNAS May 30 2917; vol.114; no.22: E4511–E4519
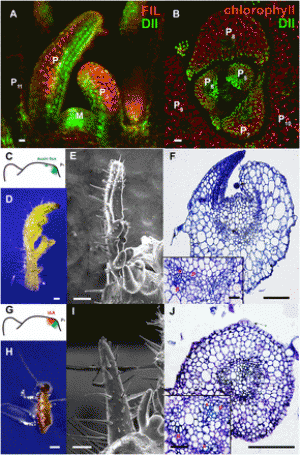
Fig. 1. Fruit-ripening phenotypes of tomato sldml2 mutants. (A) Plants of the WT (cv. Micro-Tom), sldml2-1, and sldml2-2 at the same stage. All plants were from the T0 generation. (B) Fruits of the WT and sldml2-1 at 46 dpa and 60 dpa. (C) Photograph of the inside of fruits of the WT and sldml2-1 at 60 dpa. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :