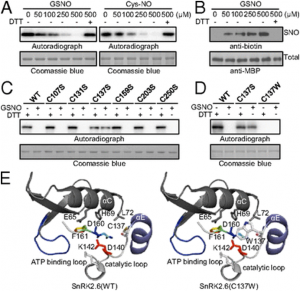
|
Geographically Distinct and Domain-Specific Sequence Variations in the Alleles of Rice Blast Resistance Gene Pib.
Wednesday, 2016/07/27 | 08:13:04
|
|
Vasudevan K, Vera Cruz CM, Gruissem W, Bhullar NK. Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 23;7:915. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00915. eCollection 2016. AbstractRice blast is caused by Magnaporthe oryzae, which is the most destructive fungal pathogen affecting rice growing regions worldwide. The rice blast resistance gene Pib confers broad-spectrum resistance against Southeast Asian M. oryzae races. We investigated the allelic diversity of Pib in rice germplasm originating from 12 major rice growing countries. Twenty-five new Pib alleles were identified that have unique single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions and/or deletions, in addition to the polymorphic nucleotides that are shared between the different alleles. These partially or completely shared polymorphic nucleotides indicate frequent sequence exchange events between the Pib alleles. In some of the new Pib alleles, nucleotide diversity is high in the LRR domain, whereas, in others it is distributed among the NB-ARC and LRR domains. Most of the polymorphic amino acids in LRR and NB-ARC2 domains are predicted as solvent-exposed. Several of the alleles and the unique SNPs are country specific, suggesting a diversifying selection of alleles in various geographical locations in response to the locally prevalent M. oryzae population. Together, the new Pib alleles are an important genetic resource for rice blast resistance breeding programs and provide new information on rice-M. oryzae interactions at the molecular level.
See: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4917536/
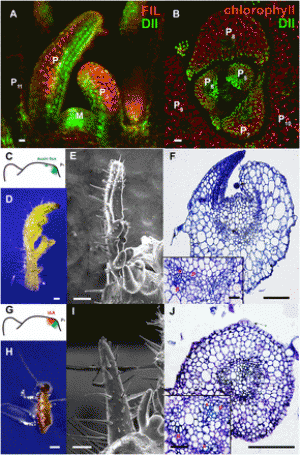
Selection of candidates for Pib allele mining. Accessions from 12 major rice growing countries that were chosen based on their phenotype (score 0) in UBN and against at least two of the five pure blast isolates are presented (A). The accessions that are molecular positives for Pib based on Nsb marker screening were chosen as candidates, and the candidates from which Pib was successfully amplified are also presented. Sample picture of molecular screening of rice accessions for selection of Pib allele mining candidates is shown (B). 1 kb, DNA marker; LTH, negative control; Pib, positive control (Pib-monogenic line); WC, water control; 1–11, test accessions. The accessions positive for Pib are 2 (IRGC-4471), 3 (IRGC-4552), 4 (IRGC-4553), 7 (IRGC-4574), 8 (IRGC-4619), 9 (IRGC-4633), 10 (IRGC-4634), and 11 (IRGC-4642). The upper band (629 bp) indicates the presence of Pib and the lower band (∼250 bp) shows the actin band, which is an internal control for the PCR. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(39).png)