|
Plastidial metabolite MEcPP induces a transcriptionally centered stress-response hub via the transcription factor CAMTA3
Friday, 2016/08/05 | 08:28:51
|
|
Geoffrey Benn, Marta Bjornson, Haiyan Ke, Amancio De Souza, Edward I. Balmond, Jared T. Shaw, and Katayoon Dehesh SignificanceA dual-function plastidial metabolite, methylerythritol cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP), an intermediate of the plastidial pathway for isoprenoids production and a retrograde signaling metabolite, transduces signals to activate general stress-response (GSR) genes by inducing a transcriptionally centered stress hub. Specifically, MEcPP mediates the induction of the rapidly and transiently stress-responsive functional cis-element rapid stress response element via the calmodulin-binding transcriptional activator CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTION ACTIVATOR 3 in a calcium-dependent manner. MEcPP-mediated induction of this hard-wired GSR circuitry is a prime example of the integration of this metabolite into transcriptional networks and, by extension, modulation of downstream responses such as protein-folding capacity. This finding provides a foundation for investigating mechanisms of biological responses to stress and the roles of metabolites beyond the expected classical biochemical pathways. AbstractThe general stress response (GSR) is an evolutionarily conserved rapid and transient transcriptional reprograming of genes central for transducing environmental signals into cellular responses, leading to metabolic and physiological readjustments to cope with prevailing conditions. Defining the regulatory components of the GSR will provide crucial insight into the design principles of early stress-response modules and their role in orchestrating master regulators of adaptive responses. Overaccumulation of methylerythritol cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP), a bifunctional chemical entity serving as both a precursor of isoprenoids produced by the plastidial methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway and a stress-specific retrograde signal, in ceh1 (constitutively expressing hydroperoxide lyase1)-mutant plants leads to large-scale transcriptional alterations. Bioinformatic analyses of microarray data in ceh1 plants established the overrepresentation of a stress-responsive cis element and key GSR marker, the rapid stress response element (RSRE), in the promoters of robustly induced genes. ceh1 plants carrying an established 4×RSRE:Luciferase reporter for monitoring the GSR support constitutive activation of the response in this mutant background. Genetics and pharmacological approaches confirmed the specificity of MEcPP in RSRE induction via the transcription factor CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTION ACTIVATOR 3 (CAMTA3), in a calcium-dependent manner. Moreover, CAMTA3-dependent activation of IRE1a (inositol-requiring protein-1) and bZIP60 (basic leucine zipper 60), two RSRE containing unfolded protein-response genes, bridges MEcPP-mediated GSR induction to the potentiation of protein-folding homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. These findings introduce the notion of transcriptional regulation by a key plastidial retrograde signaling metabolite that induces nuclear GSR, thereby offering a window into the role of interorgannellar communication in shaping cellular adaptive responses.
See http://www.pnas.org/content/113/31/8855.full PNAS August 2 2016; vol.113; no.31: 8855–8860
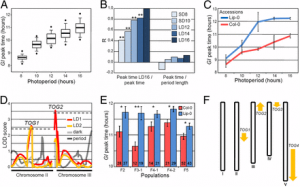
Fig. 1. The constitutive activation of GSR is specific to the ceh1 and does not depend on SA. (A) Proportion of DEGs in the ceh1 mutant containing an RSRE in the proximal 500 bp of the promoter region. The dashed line represents the proportion of genes on the ATH1 genome array with RSRE-containing promoters. P values were determined via the hypergeometric distribution. (B) Enrichment of selected GO terms in RSRE-containing genes induced in ceh1 (observed); P values were determined using false-discovery rate (FDR)-corrected Fisher’s exact test. (C) Basal RSRE:LUC activity in parent (P) and ceh1 seedlings. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 123) with the P value determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test. (D) Representative darkfield images of P and ceh1 plants expressing RSRE:LUC. (E) Basal RSRE:LUC activity in the listed genotypes. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n ≥ 123). Bars that do not share a letter represent statistically significant differences as determined by Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test (P < 0.05). (F) Representative darkfield images of plants of each genotype expressing RSRE:LUC. The color-coded bar displays the intensity of LUC activity. |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(43).png)