Studies of antibiotic resistance are usually initiated in earnest only after resistance has become established in clinical pathogens. Here, we forewarn of a resistance mechanism to the novel antibiotics ketolides, which are only coming into broad medical practice. We show that the balanced activities and coordinated expression of two genes, pikR1 and pikR2
Persons living in the tropics and subtropics are at risk for dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever, and large epidemics occur unexpectedly that can overburden healthcare systems. The spatial and temporal dynamics of dengue transmission are poorly understood, limiting disease control efforts. We compiled a large-scale dataset and analyzed continental-scale patterns of dengue in Southeast Asia.
Grain size is a dominant component of grain weight in cereals. Earlier studies have shown that OsGS5 plays a major role in regulating both grain size and weight in rice via promotion of cell division. In this study, we isolated TaGS5 homoeologues in wheat and mapped them on chromosomes 3A, 3B and 3D. Temporal and spatial expression analysis showed that TaGS5 homoeologues were preferentially expressed in young spikes and developing grains
Savannas account for 20% of global land area and support 30% of terrestrial net primary production. The biome is characterized by the coexistence of trees and grasses. Tree abundance strongly influences savanna ecosystem dynamics. Maximum tree abundance in tropical savannas is found to be negatively correlated with rainfall intensity, which remains unexplained.
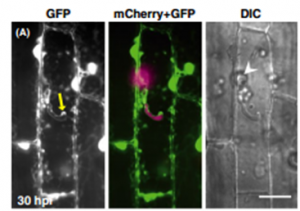
The rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae grows inside living host cells. Cytological analyses by live-cell imaging have revealed characteristics of the biotrophic invasion, particularly the extrainvasive hyphal membrane (EIHM) originating from the host plasma membrane and a host membrane-rich structure, biotrophic interfacial complex (BIC). Here, we observed rice subcellular changes associated with invasive hyphal growth using various transformants expressing specifically localized fluorescent proteins.
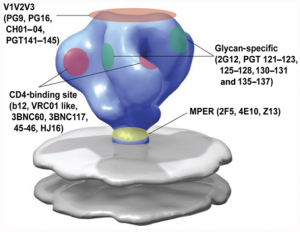
The broadly neutralizing anti–HIV-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) PG9 requires multiple posttranslational modifications to exhibit its full biological activity, including proper N-glycosylation and tyrosine sulfation. We now describe a technology that permits the controlled synthesis of these modifications in Nicotiana benthamiana. This technology allowed us to show that sulfated PG9 neutralizes HIV-1 with much higher potency than unsulfated antibody
A total of six markers RM3586 and RM160 on chromosome 3 and RM3735, RM3471, RM3687 and RM3536 on chromosome 4 were used to select promising lines in backcrossing populations for heat tolerance at flowering stage in rice. Fifty lines selected in BC3F2, BC4F1, and BC4F2 and parents were planted in 2013, and 2014 dry seasons at the CLRRI field under natural heat stress and greenhouse to evaluate heat tolerance at the reproductive period.
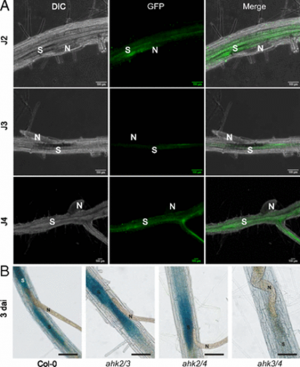
Sedentary plant-parasitic cyst nematodes are microscopic roundworms that cause significant yield losses in agriculture. Successful parasitism is based on the formation of a hypermetabolic feeding site in host roots from which the nematodes withdraw their nutrients. The host cell cycle is activated at the site of infection and contributes to the formation of the syncytium. Here, we provide genetic evidence that nematode-derived cytokinin is involved in activating the host cell cycle during infection.
There has been a critical knowledge gap for national biological C sequestration potential assessment due to a lack of relevant information about federal lands that cover nearly 30% of the whole US territory. Here, we present the results from a multimodel simulation approach and fill the current knowledge gap by revealing the C sequestration potential of federal lands across the conterminous United States and their contribution to the national ecosystem C budget through 2050.
Erigeron breviscapus, a medicinal herb used in China, is a self-incompatible species of Asteraceae. However, the genetics of its SI responses remain unknown. To better understand SI, Wei Zhang and Xiang Wie of Yunnan Agricultural University and Honghe University, respectively, performed a transcriptomic analysis of E. breviscapus after self- and cross-pollination.


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :