|
Silencing of DND1 in potato and tomato impedes conidial germination, attachment and hyphal growth of Botrytis cinerea
Monday, 2017/12/18 | 07:54:50
|
|
Kaile Sun, Ageeth van Tuinen, Jan A. L. van Kan, Anne-Marie A. Wolters, Evert Jacobsen, Richard G. F. Visser and Yuling Ba BMC Plant Biology BMC series – open in 6 December 2017, inclusive and trusted 2017 17:235 AbstractBackgroundBotrytis cinerea, a necrotrophic pathogenic fungus, attacks many crops including potato and tomato. Major genes for complete resistance to B. cinerea are not known in plants, but a few quantitative trait loci have been described in tomato. Loss of function of particular susceptibility (S) genes appears to provide a new source of resistance to B. cinerea in Arabidopsis. ResultsIn this study, orthologs of Arabidopsis S genes (DND1, DMR6, DMR1 and PMR4) were silenced by RNAi in potato and tomato (only for DND1). DND1 well-silenced potato and tomato plants showed significantly reduced diameters of B. cinerea lesions as compared to control plants, at all-time points analysed. Reduced lesion diameter was also observed on leaves of DMR6 silenced potato plants but only at 3 days post inoculation (dpi). The DMR1 and PMR4 silenced potato transformants were as susceptible as the control cv Desiree. Microscopic analysis was performed to observe B. cinerea infection progress in DND1 well-silenced potato and tomato leaves. A significantly lower number of B. cinerea conidia remained attached to the leaf surface of DND1 well-silenced potato and tomato plants and the hyphal growth of germlings was hampered. ConclusionsThis is the first report of a cytological investigation of Botrytis development on DND1-silenced crop plants. Silencing of DND1 led to reduced susceptibility to Botrytis, which was associated with impediment of conidial germination and attachment as well as hyphal growth. Our results provide new insights regarding the use of S genes in resistance breeding.
See: https://bmcplantbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12870-017-1184-2
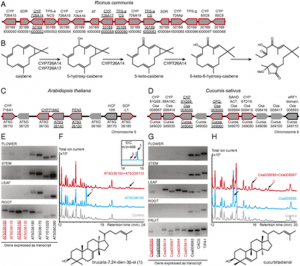
Figure 1: Detached leaf assay (DLA) of potato RNAi transformants with Botrytis cinerea (strain B05.10). a and b Lesion diameter on the inoculated leaves of the RNAi transformants. a Results from one of the two independent experiments performed for StDMR1, StDMR6 and StPMR4 (two independent well-silenced transformants per gene were used in each experiment); b Results from one of the three independent experiments for StDND1. Four independent transformants were used, one weakly-silenced transformant (−), and three well-silenced transformants (+). Susceptible control was cv Desiree. The average of all lesion diameters per transformant per time point is provided. Asterisks indicate degree of significance compared to cv Desiree plants (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001); c B. cinerea disease symptoms on cv Desiree and StDND1-silenced transformants. Photos were taken at 3 days post inoculation (dpi) |
|
|
|
[ Other News ]___________________________________________________
|


 Curently online :
Curently online :
 Total visitors :
Total visitors :
(19).png)